Accounting localization in Odoo 17
Accounting localization is the process of managing an accounting system as per specific country requirements and accounting standards. In short, it allows you to customize the product to your country’s specific financial requirements. Localization allows the automation of several accounting processes as per regional norms.
The following are the attributes it covers such as:
- Automated tax calculation.
- The creation of complaint reports and invoices.
- Integration with local e-invoicing systems, when applicable.
Accounting localization saves your accountants time and money by automating processes and regional standards. They can shift their focus from data entry and compliance assurance to more strategic duties. In this blog, we will look at the localization elements of Japanese companies.
Localization for Japan in Odoo 17
To set up Odoo’s Japanese localization, we must first set up a Japanese company. To do this, go to Odoo’s General Settings, the Users and Companies menu, and the Companies sub-menu.
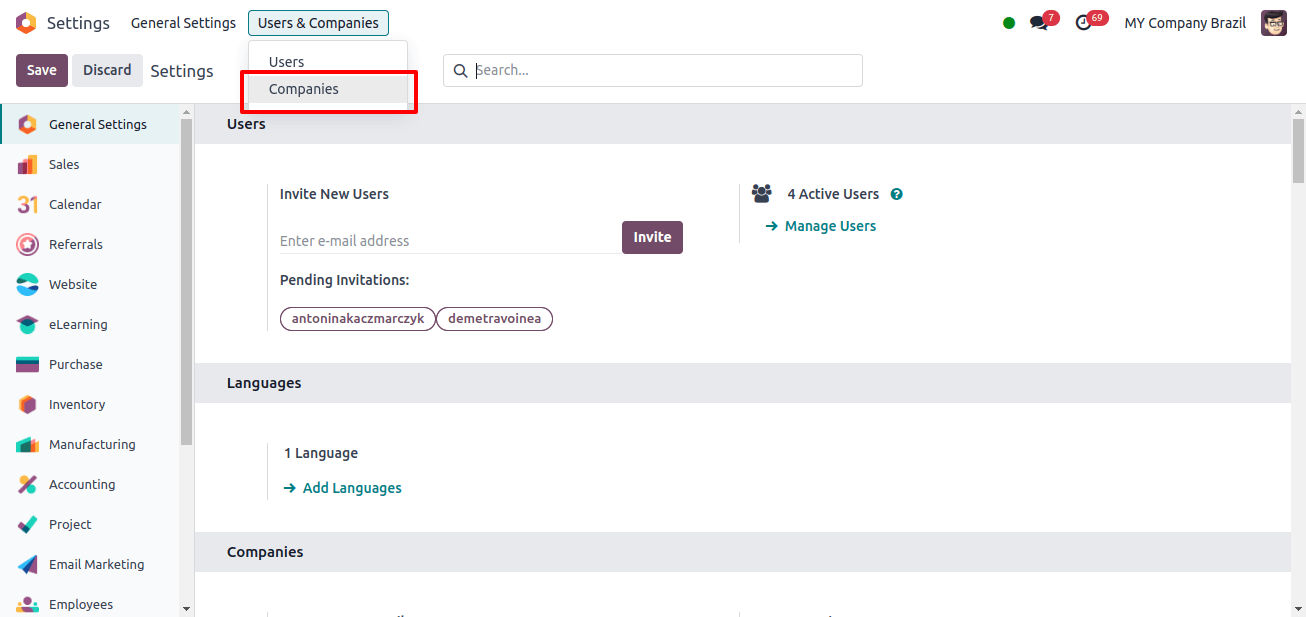
Clicking the ‘Companies’ sub-menu displays a list of all previously created companies; to add a new company, click the ‘New’ option.
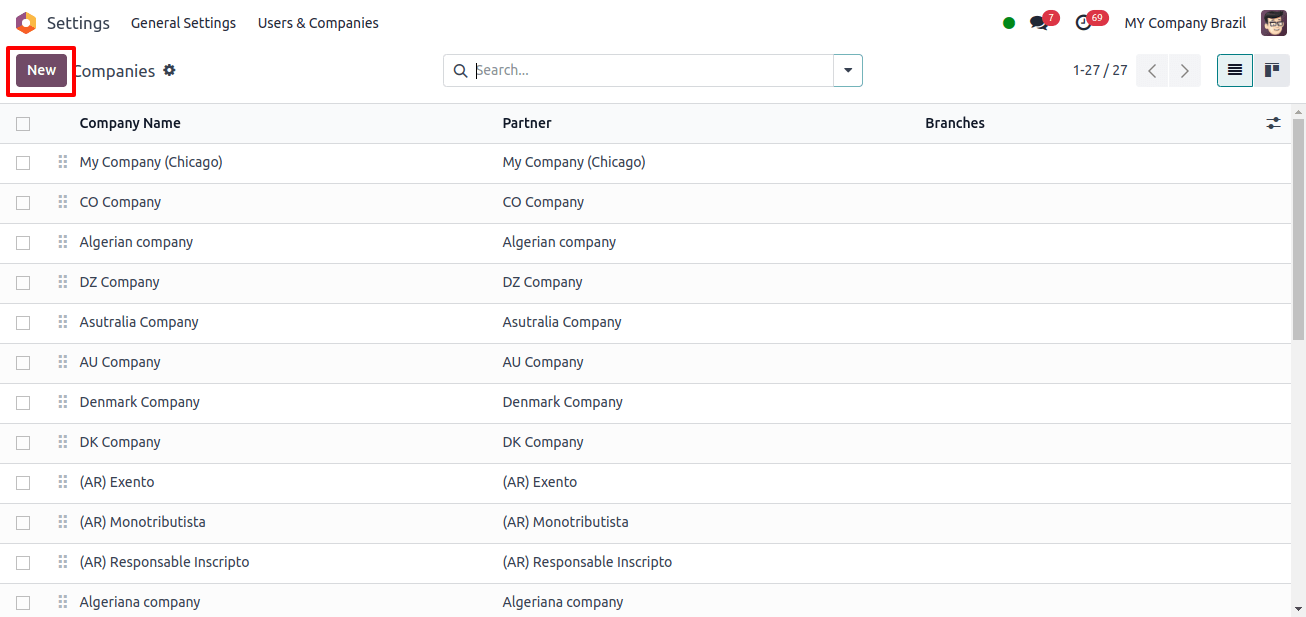
When we select the ‘New’ button, a form with the details of the new company will appear for us to complete.
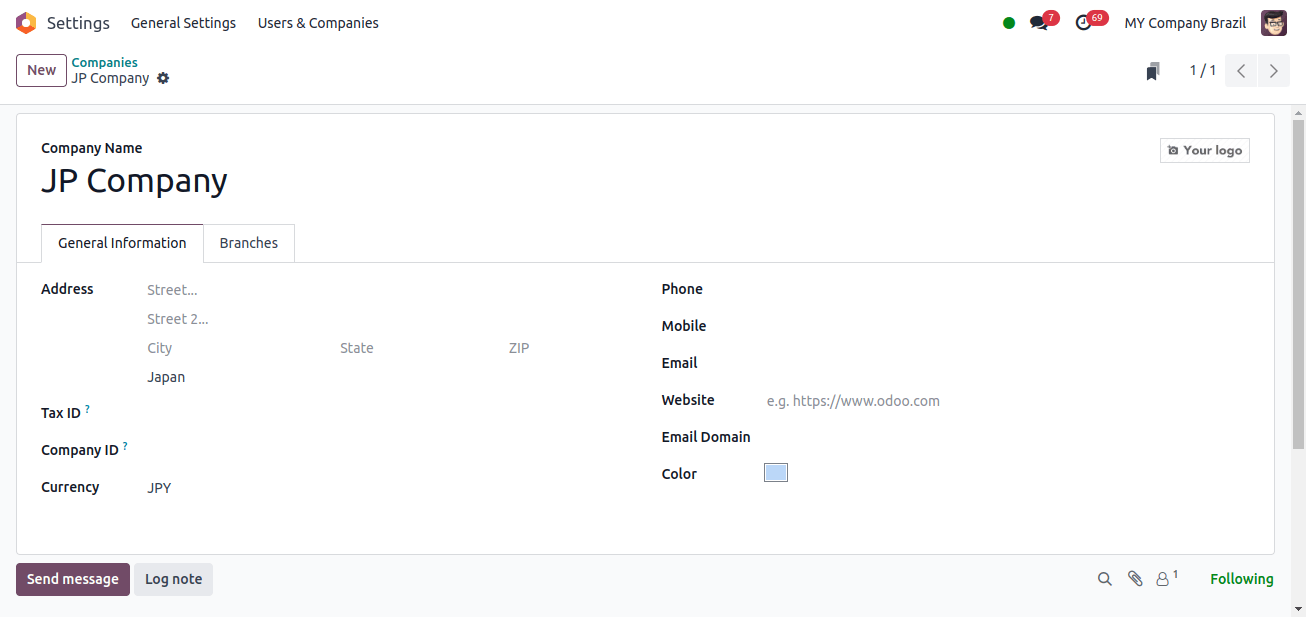
Once all settings have been correctly entered, click the save button to save the company information.
We know that the official currency in Japan is the Japanese yen, when we enter the country name in the company’s address, Odoo automatically sets the currency to Japanese Yen.
The next step is to create a localization package for this company. Open Odoo 17’s accounting application and go to Configuration > Settings.
In the Fiscal Localization field, we may configure the localization package. After selecting Japan as the package, click the ‘Save’ button.
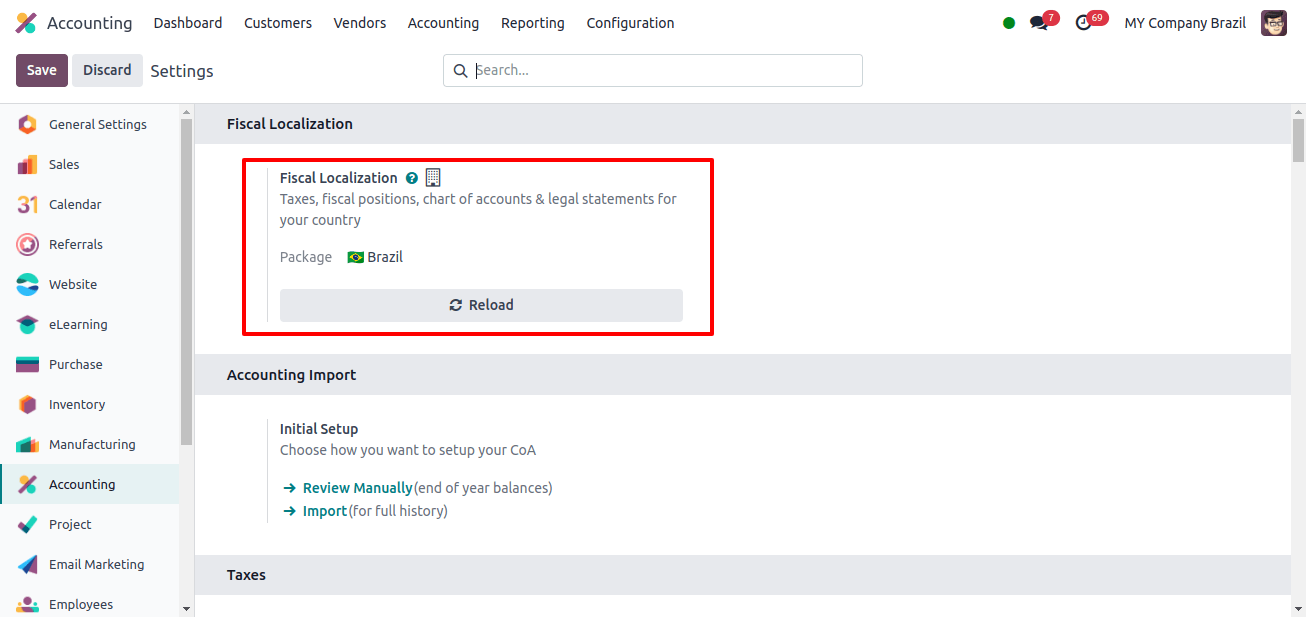
Changes occur when Japanese localization is configured.
When the company’s localization was adjusted to Japanese, many changes were obvious. Some of the primary setups in Odoo include the fiscal position, chart of accounts, taxes, journal entries, and so on.
When a localization package is assigned, the indicated properties, such as CoA, taxes for conducting business in that nation, Journals, and fiscal positions, are pre-installed.
Fiscal position: In Odoo, a fiscal position is a set of rules that specify how accounts and taxes are applied to transactions based on many factors such as the customer’s location, the nature of the business, the type of goods, and so on. Simply defined, it helps in the management of tax and accounting issues arising from several different countries.
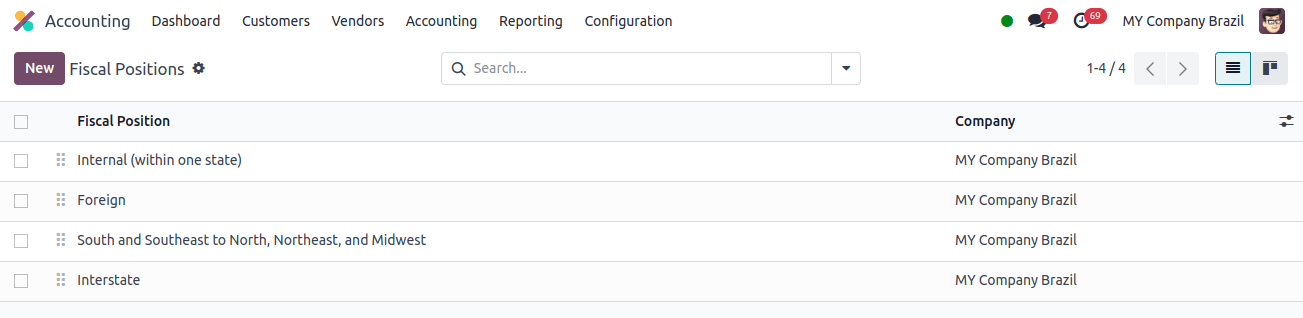
Chart of Accounts: The chart of accounts is an integral part of Odoo’s accounting module. It serves as a list of all the accounts used to track your company’s financial operations. Companies from different countries may use distinct charts of accounts.
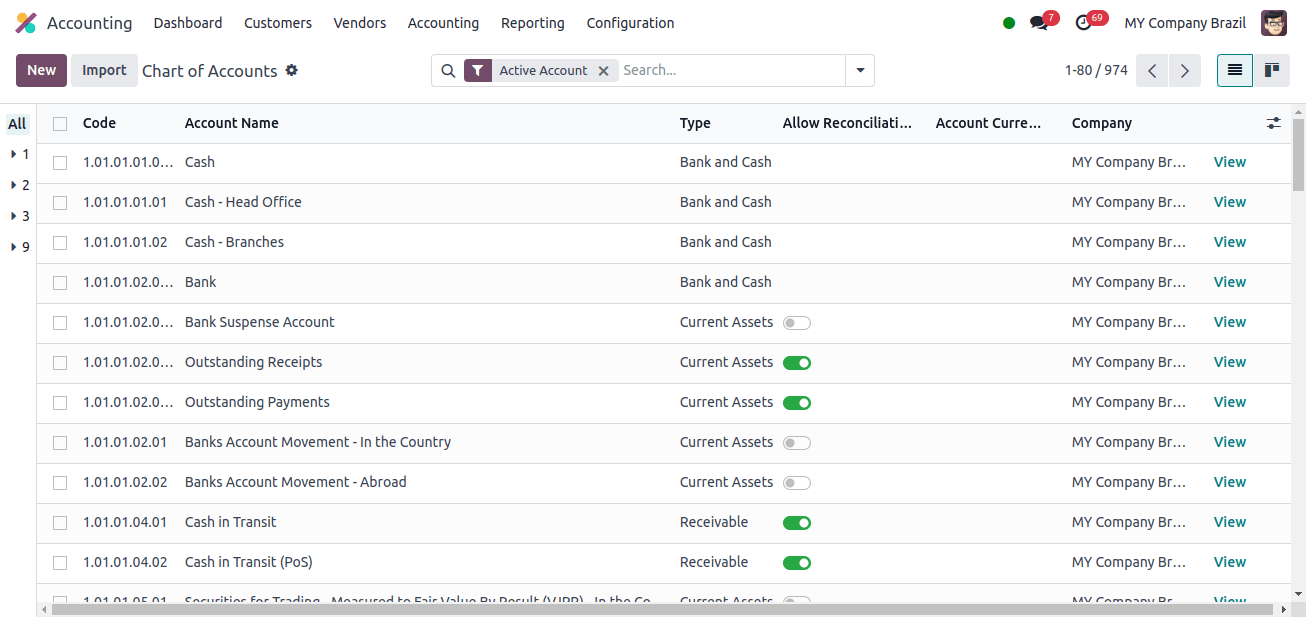
The above image shows the Chart of Accounts used by Japanese companies. To set up a new Chart of Accounts for this company, select the New option and enter the necessary information.
Taxes: Taxes are charges levied on several components of a commercial transaction. Odoo’s tax capabilities allow you to automate tax computations, manage tax compliance, and ensure financial reporting accuracy. Odoo allows you to define different tax kinds, such as purchase and sales taxes, as well as the existing rates and restrictions.
When creating purchase orders or invoices, Odoo calculates the required taxes based on the vendor’s location and the items or services purchased or supplied. The Accounting application’s setup menu includes the Taxes sub-menu.
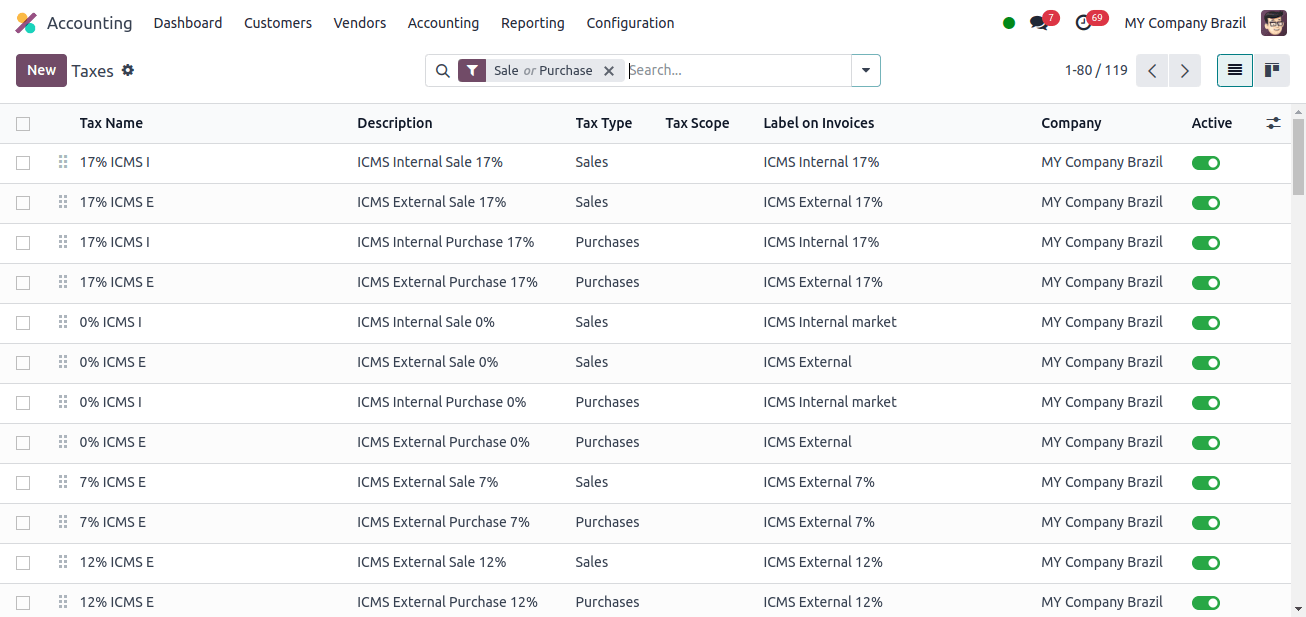
When we click the Taxes sub-menu, we can see all the pre-configured taxes for this Japanese company, which we may apply to any of our transactions. We can also add new taxes by clicking the New button.
Here, we can see two basic types of taxes; sales taxes and purchase taxes. Sales taxes are imposed on products or services when they are sold to customers, whereas purchase taxes are applied when they are purchased from a vendor.
Under the Taxes field of Configuration > Settings, we may set the company’s default taxes. There is an option to configure this manually or have Odoo set it automatically. Odoo will automatically configure the Default Taxes for the company when the Localization Package is set to Japan.
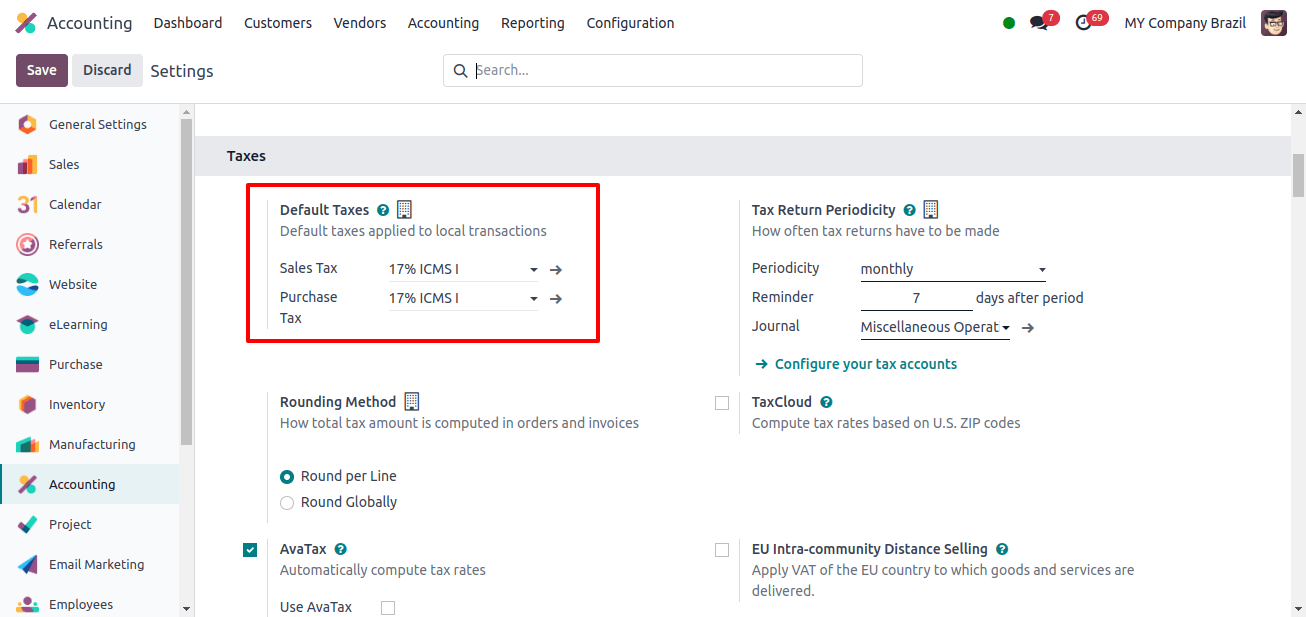
According to the image above, the default sales tax and default purchase tax applied by Japanese companies are 10% sales tax and 10% purchase tax, respectively. That is, all Japanese enterprises wish to use these taxes as the default tax in their dealings.
Journals: Journals are used in company accounting to record financial transactions. Odoo allows you to create many types of journals to manage and organize different types of your accounting system.
Each journal in Odoo can have its own set of configurations and settings, such as default accounts, journal type, sequence settings, and access privileges. These choices allow you to properly record and categorize financial activities in your Odoo instance.
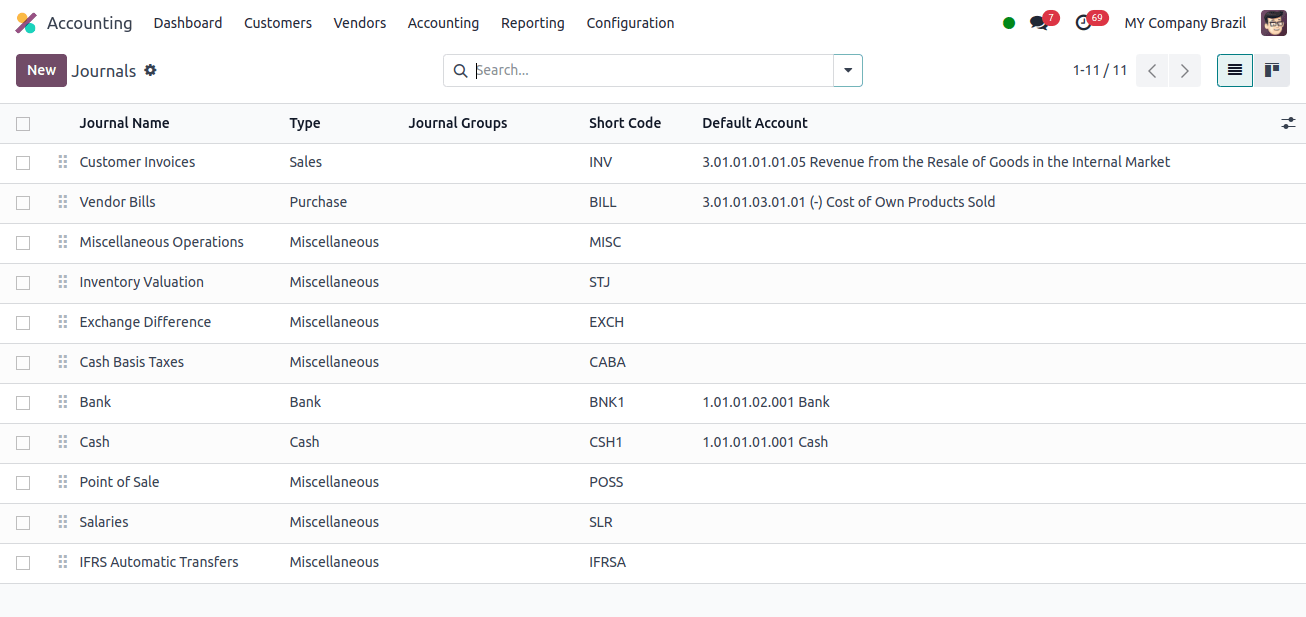
The image above shows different journals that Japanese companies use. Each journal will have an account to record transactions.
The Accounting application’s Configuration > Settings section has a space for adding the company’s fiscal nation, which is its local country, under the Taxes section.
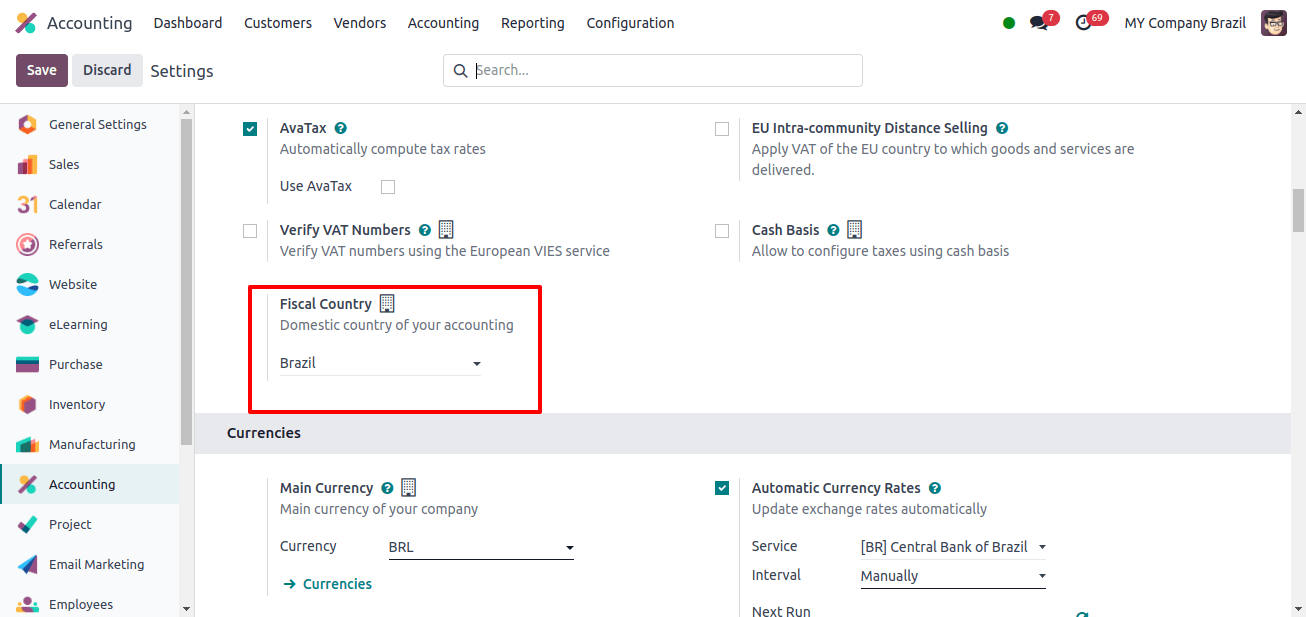
Odoo automatically set the fiscal country for the company to Japan because we selected the Japan Localization Package.
The Japanese yen is the official currency of Japan, and in Odoo, we can specify the main currency for a company by selecting it under the currencies section of the Accounting application’s Configuration settings.
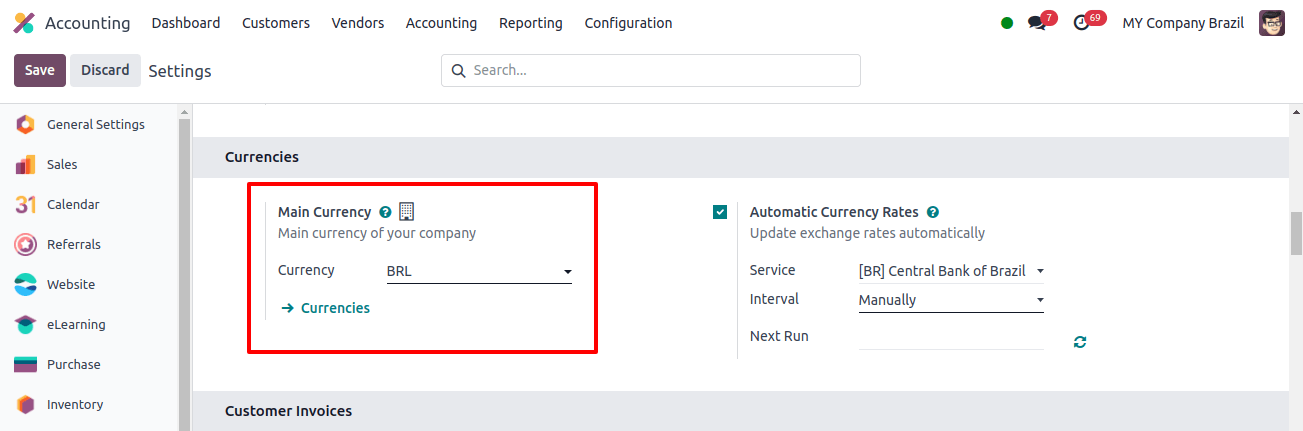
When the localization package is set to Japan, Odoo automatically selects the Japanese yen as the company’s standard currency.
When we go to the Accounting application’s Reporting menu, we can find many reports about the company’s data, such as a balance sheet, profit and loss statement, tax report, etc.
Balance sheet: A balance sheet describes a company’s financial condition by listing its assets, liabilities, and equity.
* Assets: Assets are resources that a company or individual has economically valuable and likely to deliver future benefits. Assets are a key term in financial accounting, and they are typically classified based on their type and significance in the company’s activities.
* Liabilities: Liabilities are financial commitments or debts that a company owes to other parties. Liabilities on the balance sheet show the amounts owed by the business to lenders, suppliers, creditors, and other companies.
* Equity: Equity is a company’s remaining assets after its liabilities are deducted. It is an important part of the balance sheet since it reflects the shareholders’ ownership stakes and provides information about the entity’s performance and financial status.
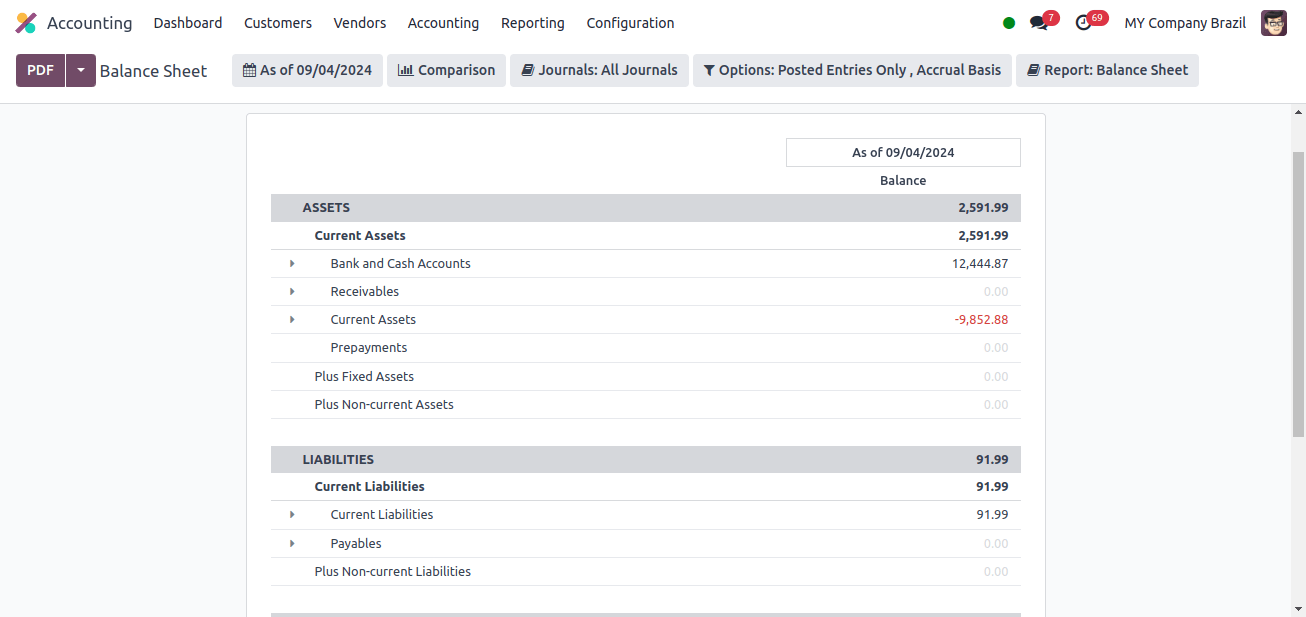
The assets field of the balance sheet includes bank and cash accounts, receivables, current assets, prepayments, fixed assets, and non-current assets, among other things. The liabilities field of the balance sheet includes current liabilities and payables, as well as non-current liabilities.
The Equity part of the balance sheet includes current year unallocated earnings, current year earnings, current year allocated earnings, prior year unallocated earnings, and retained earnings.
Profit and Loss: The company’s profit and loss report is available under the Reporting Menu. A profit and loss report is a financial statement that summarizes a company’s payments, costs, and net profits or losses during a specific period.
It provides an overview of the company’s financial performance over time and is important in establishing how profitable it is.
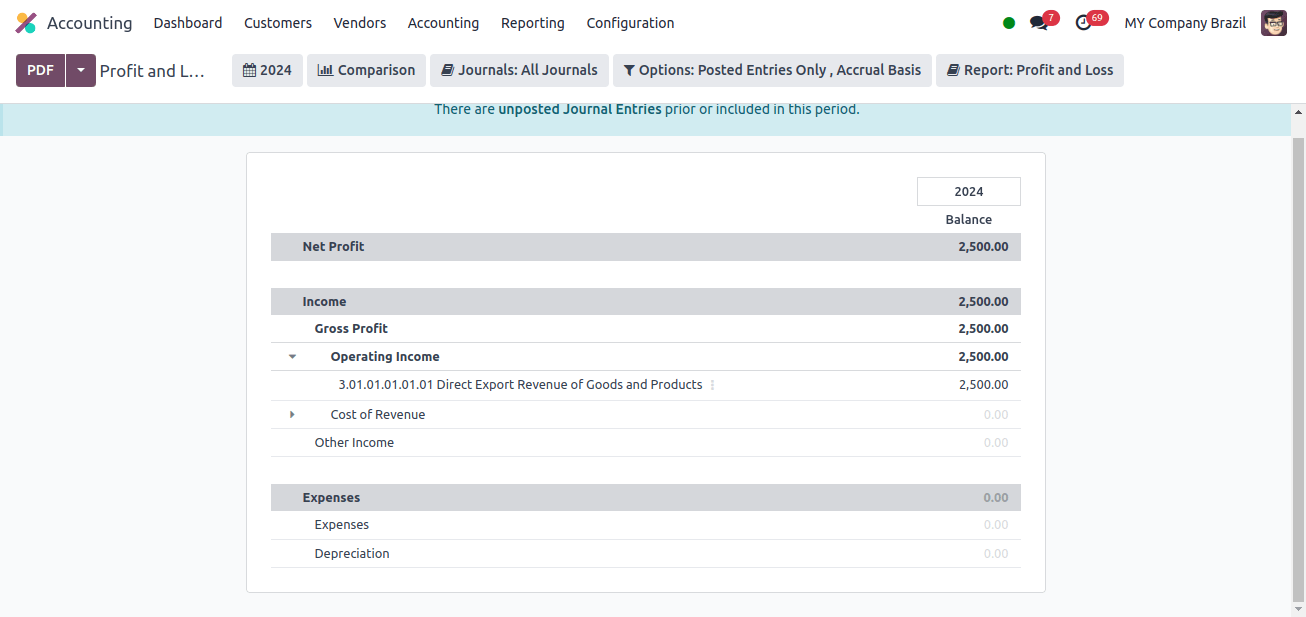
The company’s profit and loss report from Japan primarily covers gross profit, operating income, cost of revenue, other income, expenses, depreciation, and so on.
Next, we can look at the company’s tax report from Japan. A Tax Report sub-option is included in the Reporting menu. When we click the Tax Report sub-menu, we see the company’s tax report.
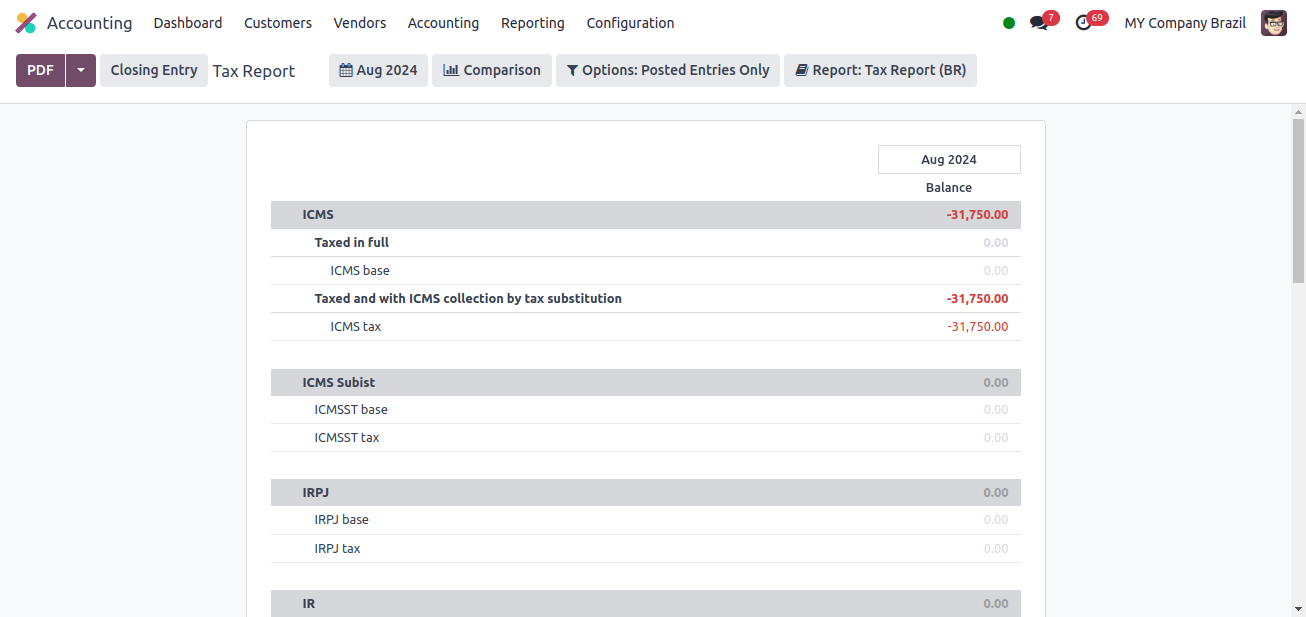
The image above displays the tax report provided by Odoo for this Japanese company over a certain period. The Odoo 17 Tax Report includes GST sales amount, GST purchase amount, sales amount, and so on.
So we’ve gone over all of the capabilities that come with Japanese Accounting localization in Odoo 17. It is now obvious that Odoo 17’s Japanese transformation ensures that complex Japanese tax regulations are followed.
This allows us to create financial reports that follow national rules and are easily understood by stakeholders and financial institutions in Japan.
Overall, Odoo 17’s accounting localization for Japan provides a comprehensive solution for business in the region. It ensures adherence, streamlines operations, improves precision and enables more informed financial decisions.


