In today’s growing business world, successful shipping operations are important for business around the globe.
Whatever the size of the organization, the ability to manage orders promptly and properly is important. Odoo 17 includes a robust tool for controlling picking policies.
Picking policies in Odoo 17 dictate how products are removed from stock for delivery when a consumer places an order. This can be done in two ways: ‘ship products as soon as they become available with back orders’ and ‘ship all products at once’.
Steps to Configure Picking Policies for Efficient Shipping in Odoo 17
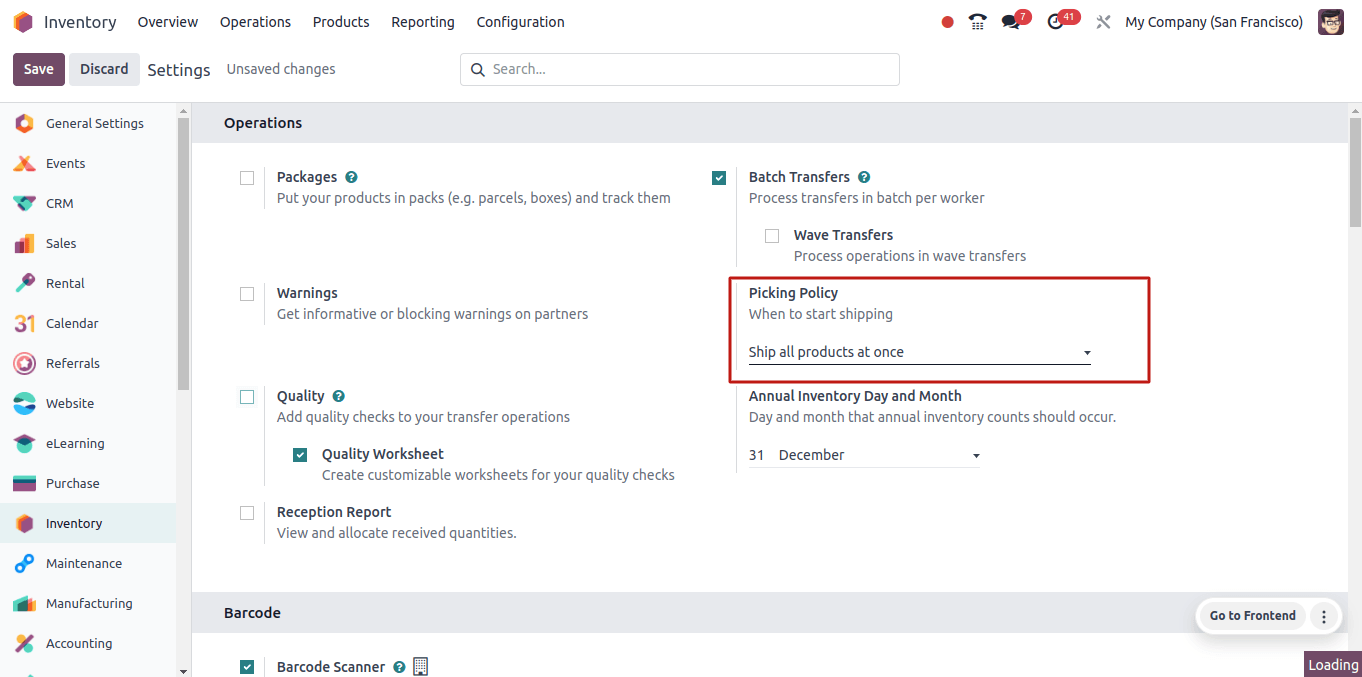
To configure the picking policy in Odoo 17, go to Inventory → Configuration → Settings.
There are two picking policy options available: Ship products as soon as they become available with back orders or ship all products at once.
With back-orders, ship things as soon as they become available.
When this selection policy is selected, the products will be dispatched as soon as they become available.
That is, if we receive an order for a product with a quantity of 10 and the product’s on-hand amount is 7, this shipping policy will ship the quantity that is now available and set a back-order for the remaining quantity.
To set this option, go to Inventory → Configuration → Settings and select the picking policy as ship products as soon as they become available, including back-orders.
A back-order is an order that cannot be completed immediately due to insufficient stock or other constraints. Odoo 17 allows you to create a back-order to track and manage any remaining items that are not available to fulfill an order.
Back orders in Odoo 17 can be managed in three ways. We can change that in the operation types by going to Inventory → Configuration → Operation Types. Select an operation type, and the create back-order option appears.
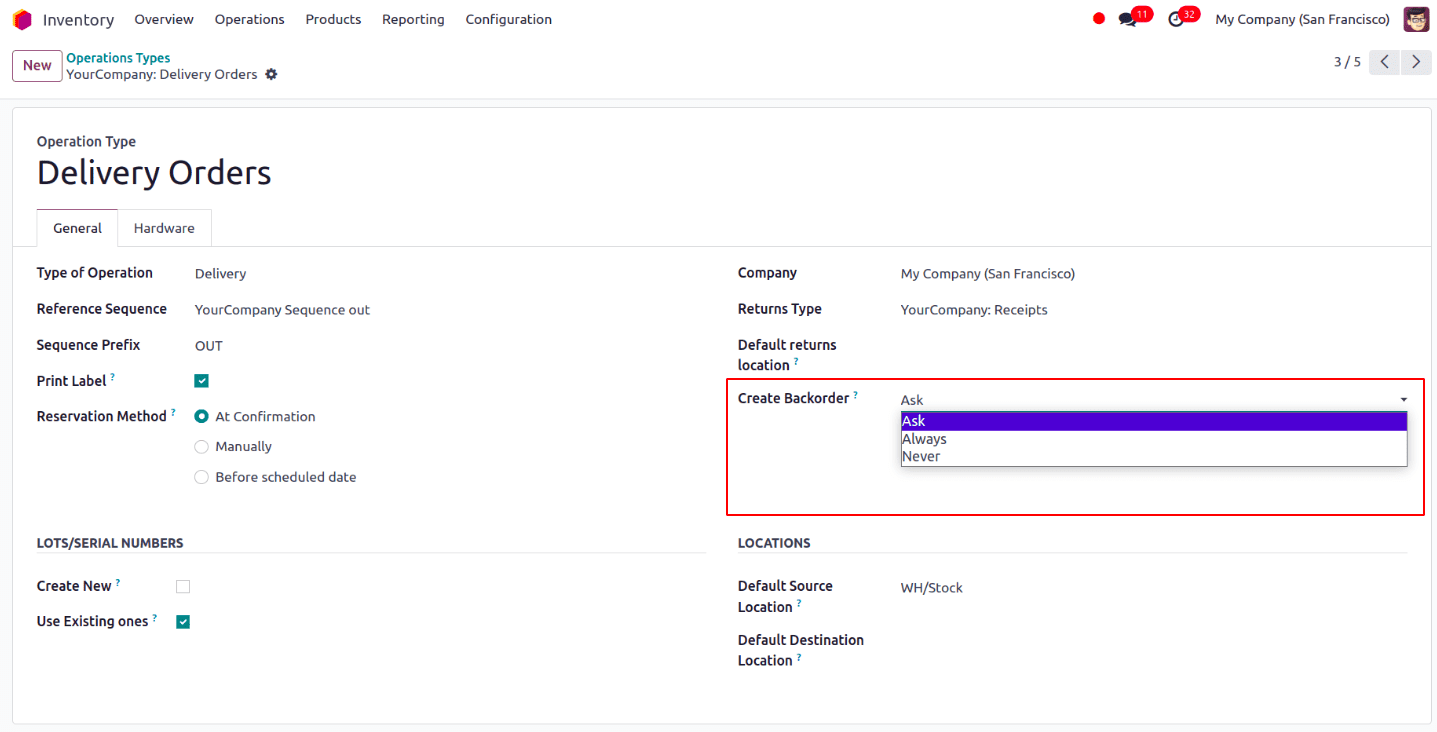
Ask: The user receives a notification asking if they want to make a backorder for the remaining products.
Always: When an order exceeds the available amount, a back-order is automatically processed for the leftover products.
Never: Back-orders are not created, and any remaining products are canceled.
We can look into the situation for Ask because we have received an order for the product wire in 15 numbers. Under the sale order’s additional information tab, we can select the shipping policy for that specific sale order.
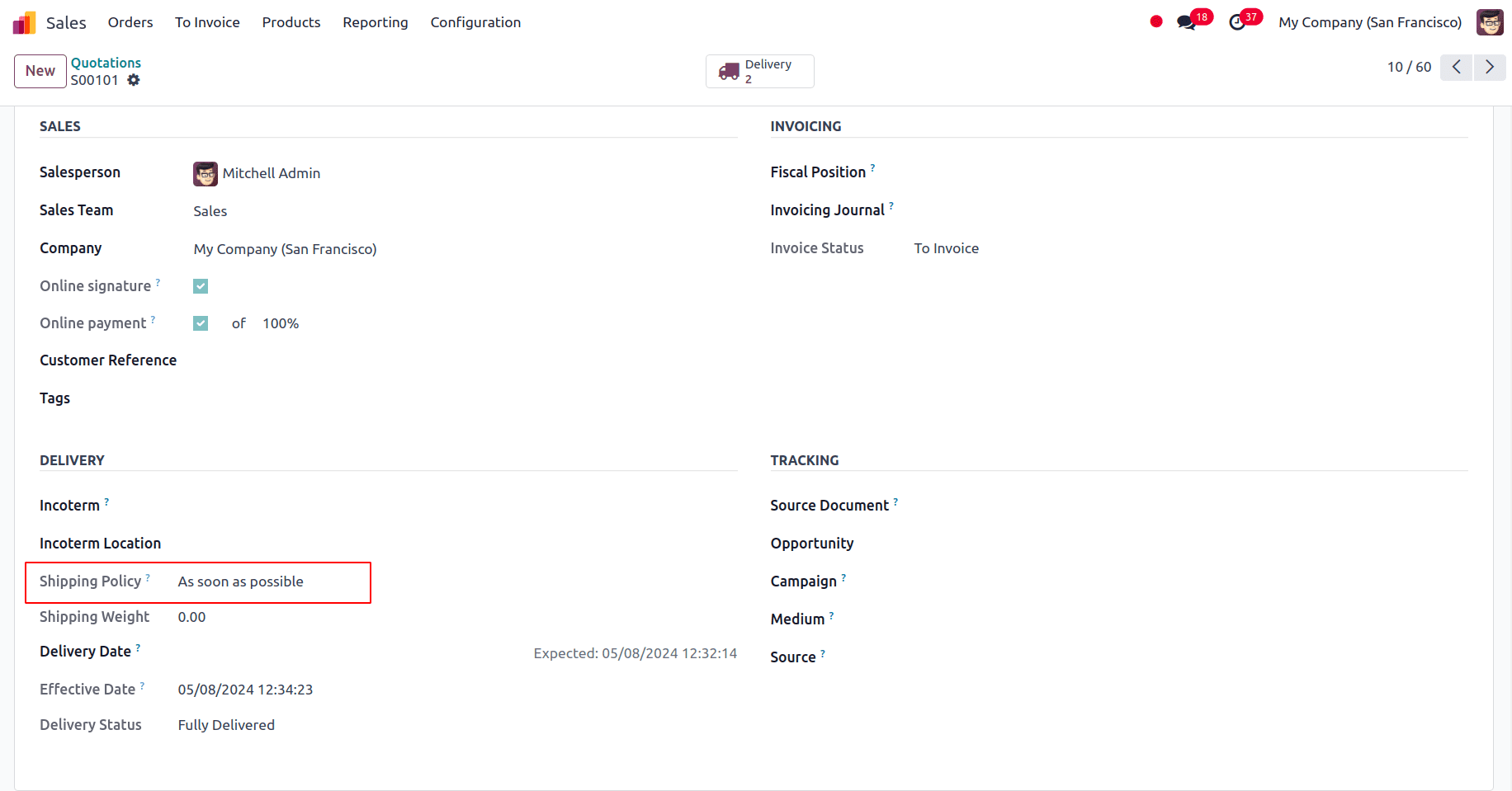
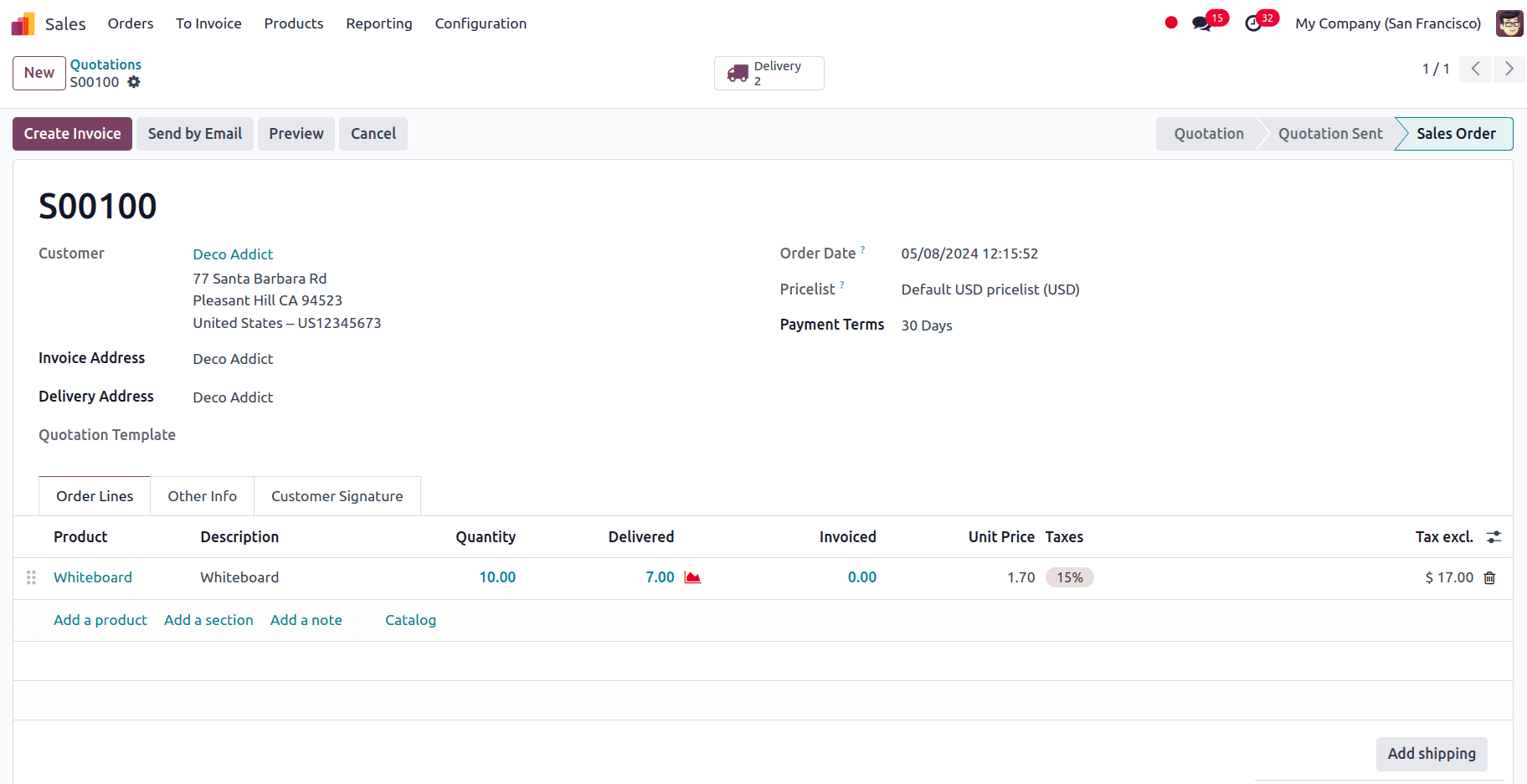
We can confirm the sales order.
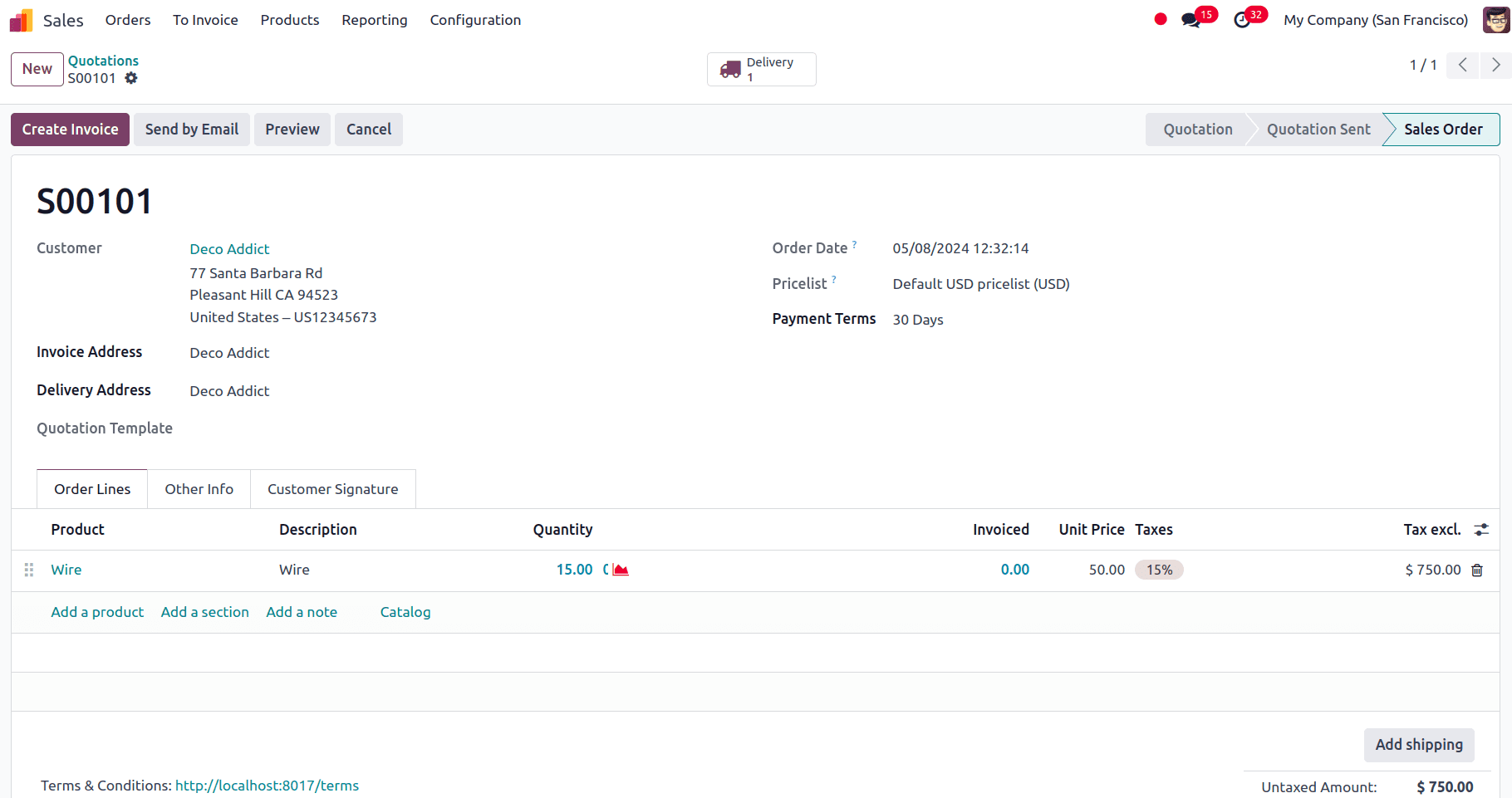
We only have 13 of the products, Wire.
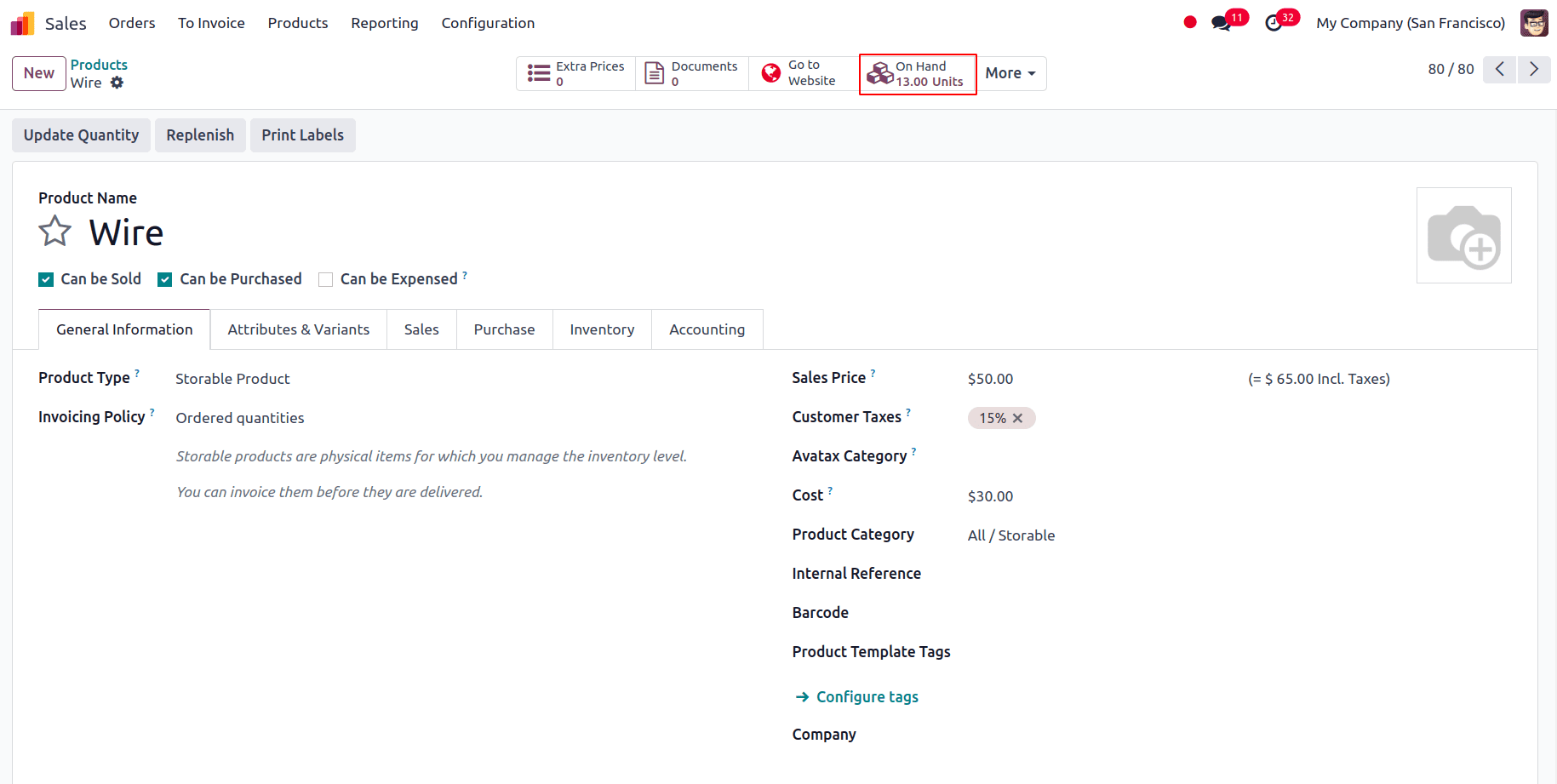
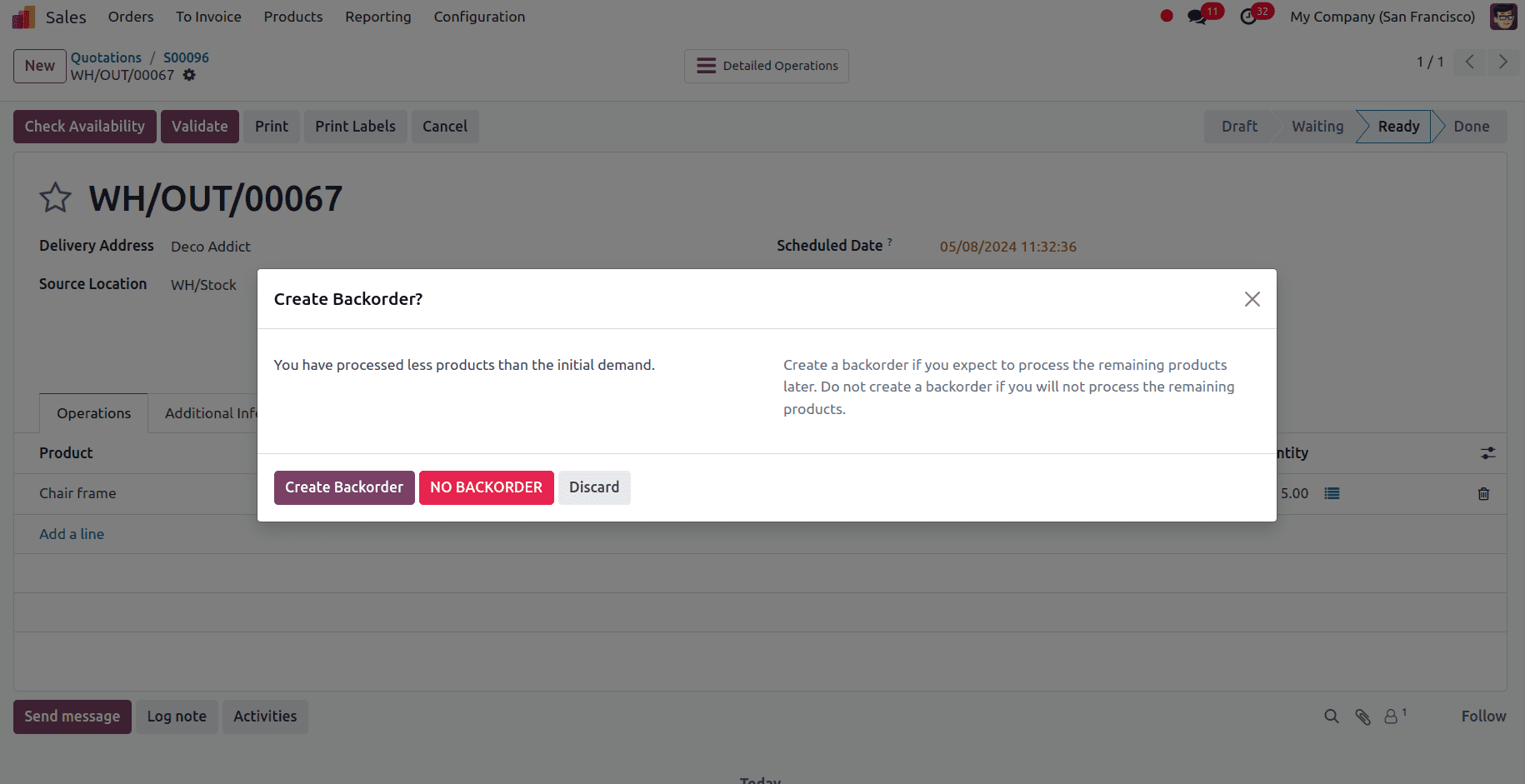
The transfer status during delivery will be READY, indicating that we are ready to transmit the things we have. After validating the delivery, a pop-up window will appear asking whether to make a backorder for the remaining products.
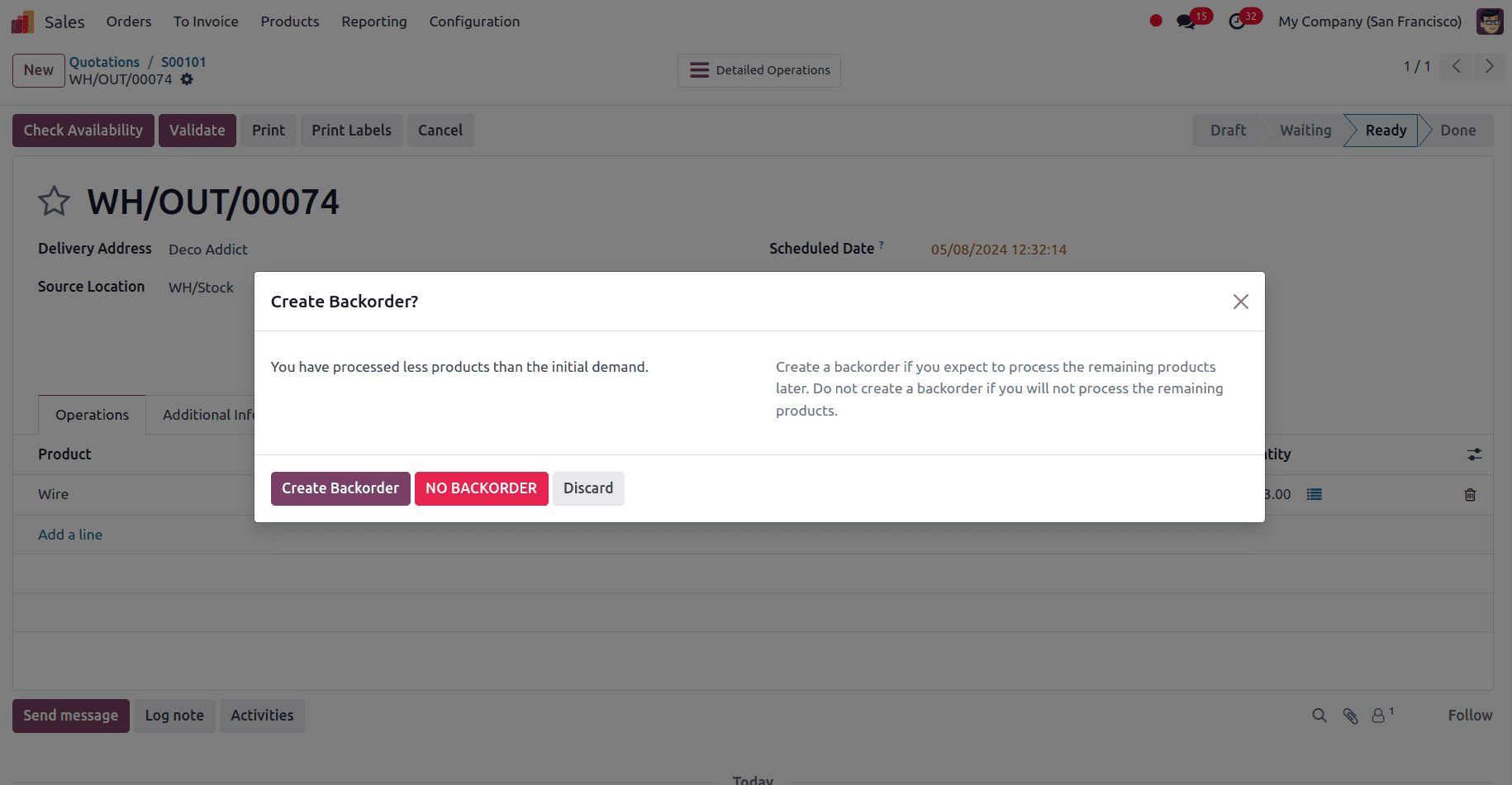
When the stock is updated, click on Create Backorder to process the remaining products, and select NO BACKORDER if we do not want to manage the remaining number.
When we click the create Backorder button, a backorder for the remaining products is displayed.
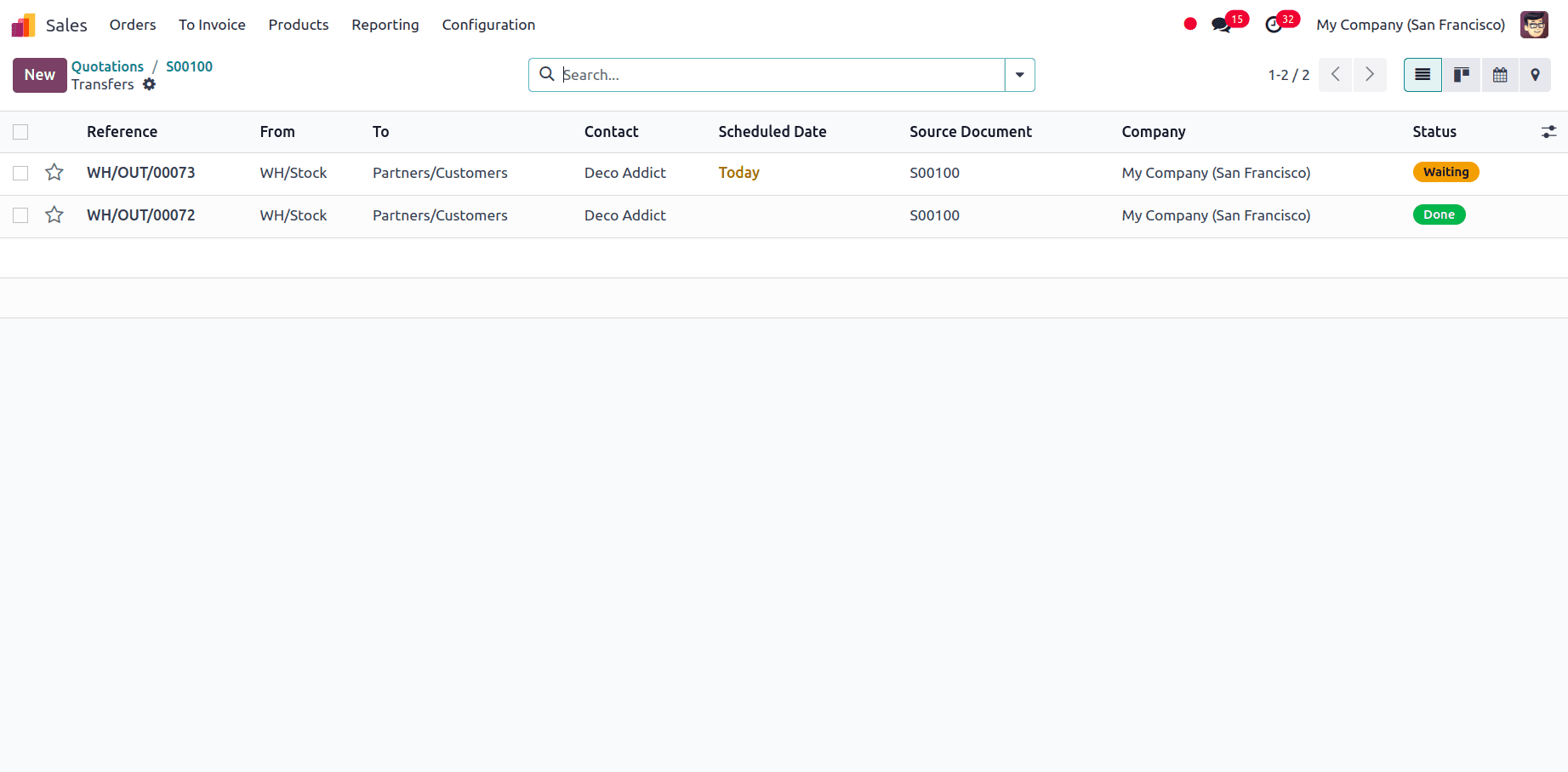
We can access the delivery smart tab and see that the delivery status for the number available is in the Done status, while the remaining quantity is in the waiting status.
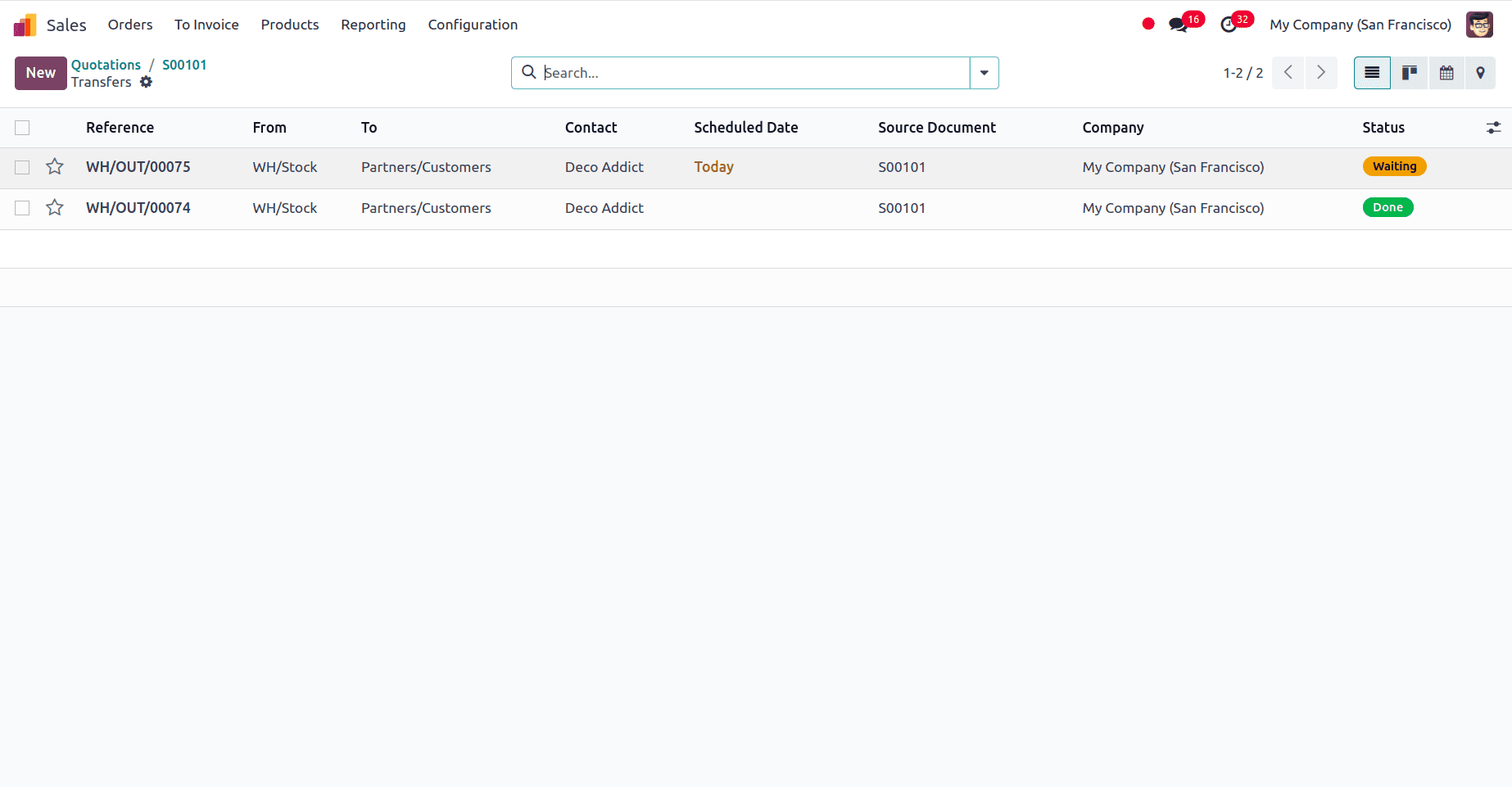
The Delivery condition for the selling order is partially delivered, as seen in the other details tab.
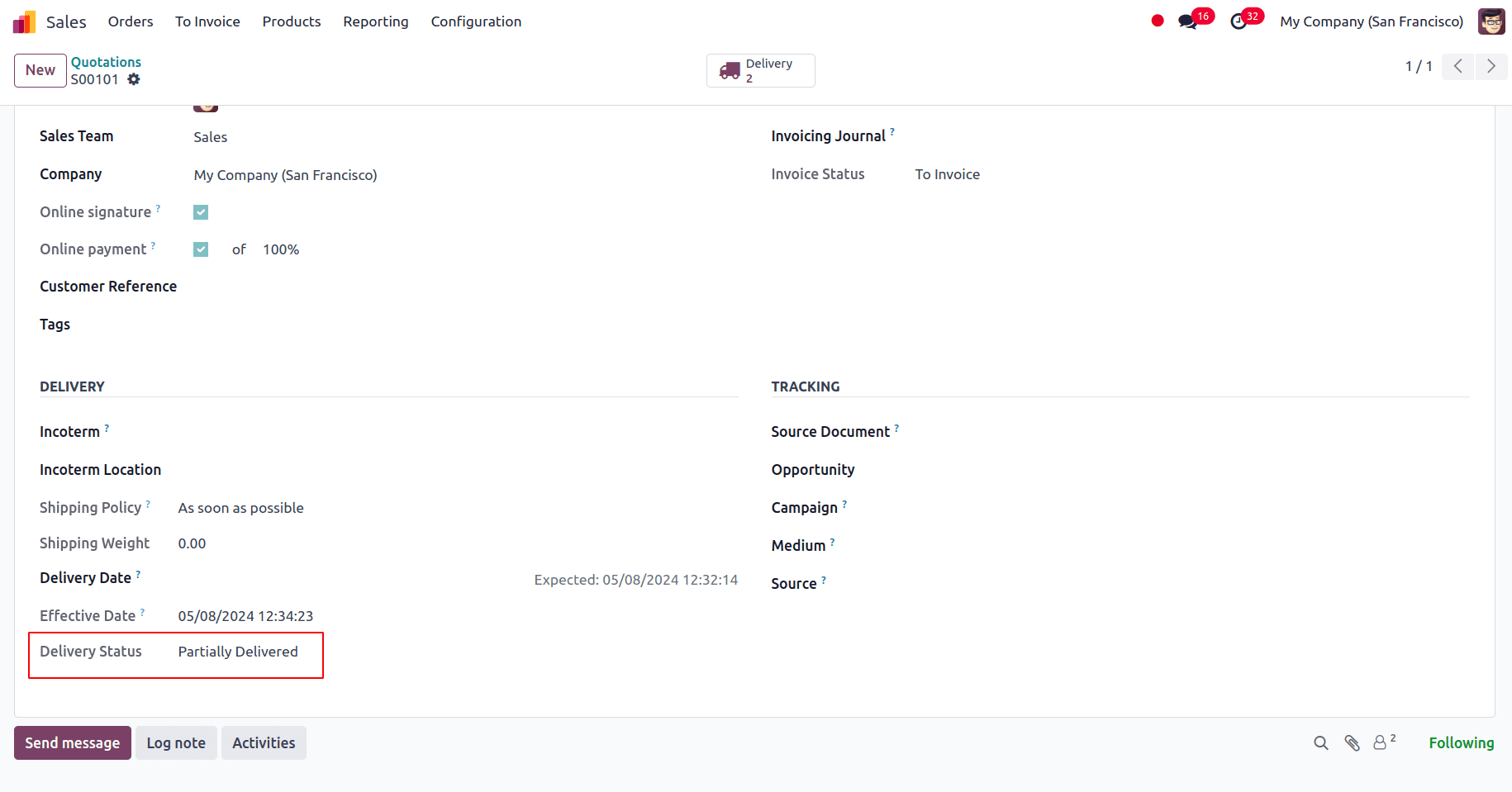
So, after the product quantity in stock is updated, the back order will be processes and the remaining quantities dispatched.
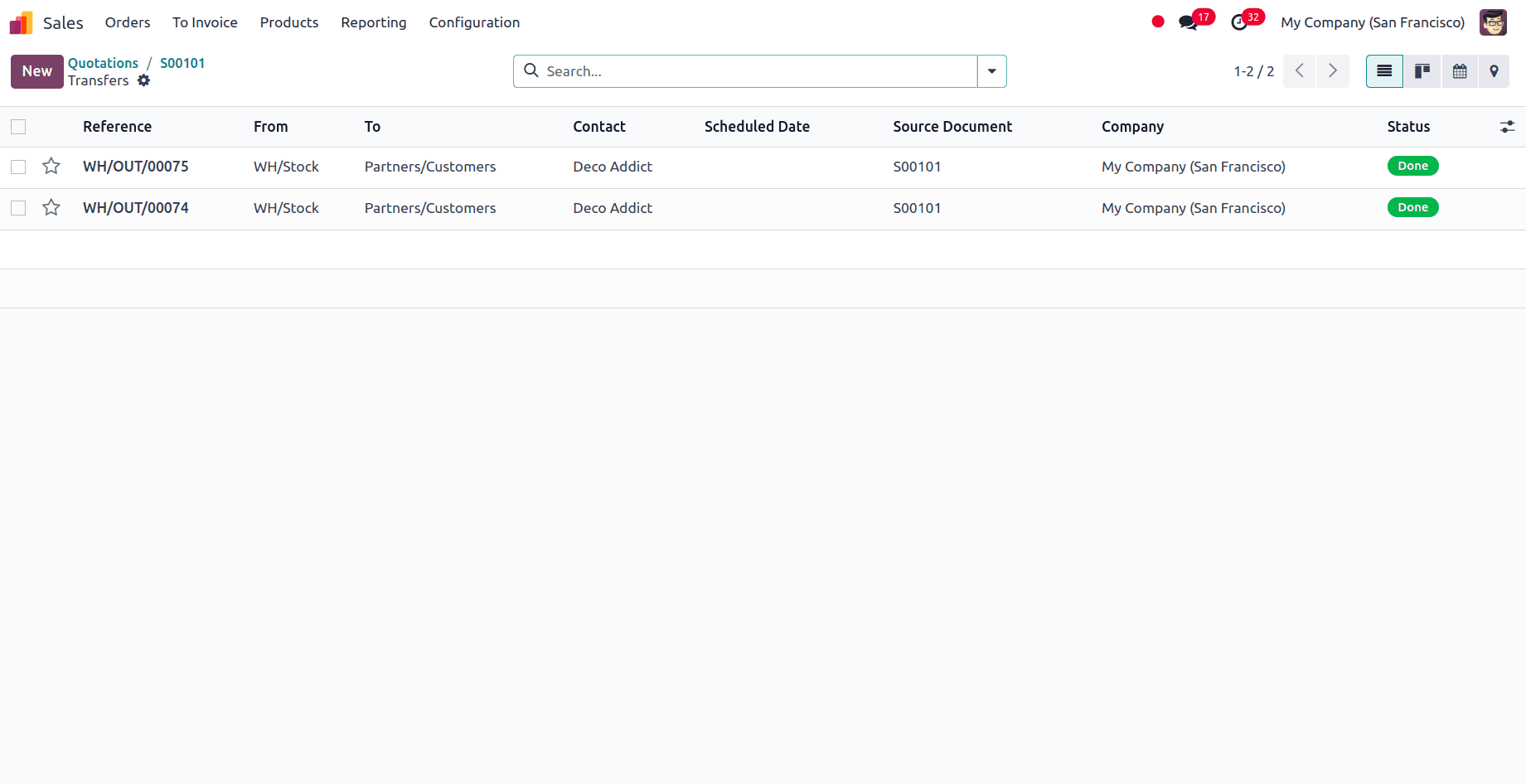
In the instance of Always, the backorder is produced automatically when we receive an order for a product in excess of the available quantity.
Let us place an order for the product Whiteboard, which has a stock quantity of 7 units.
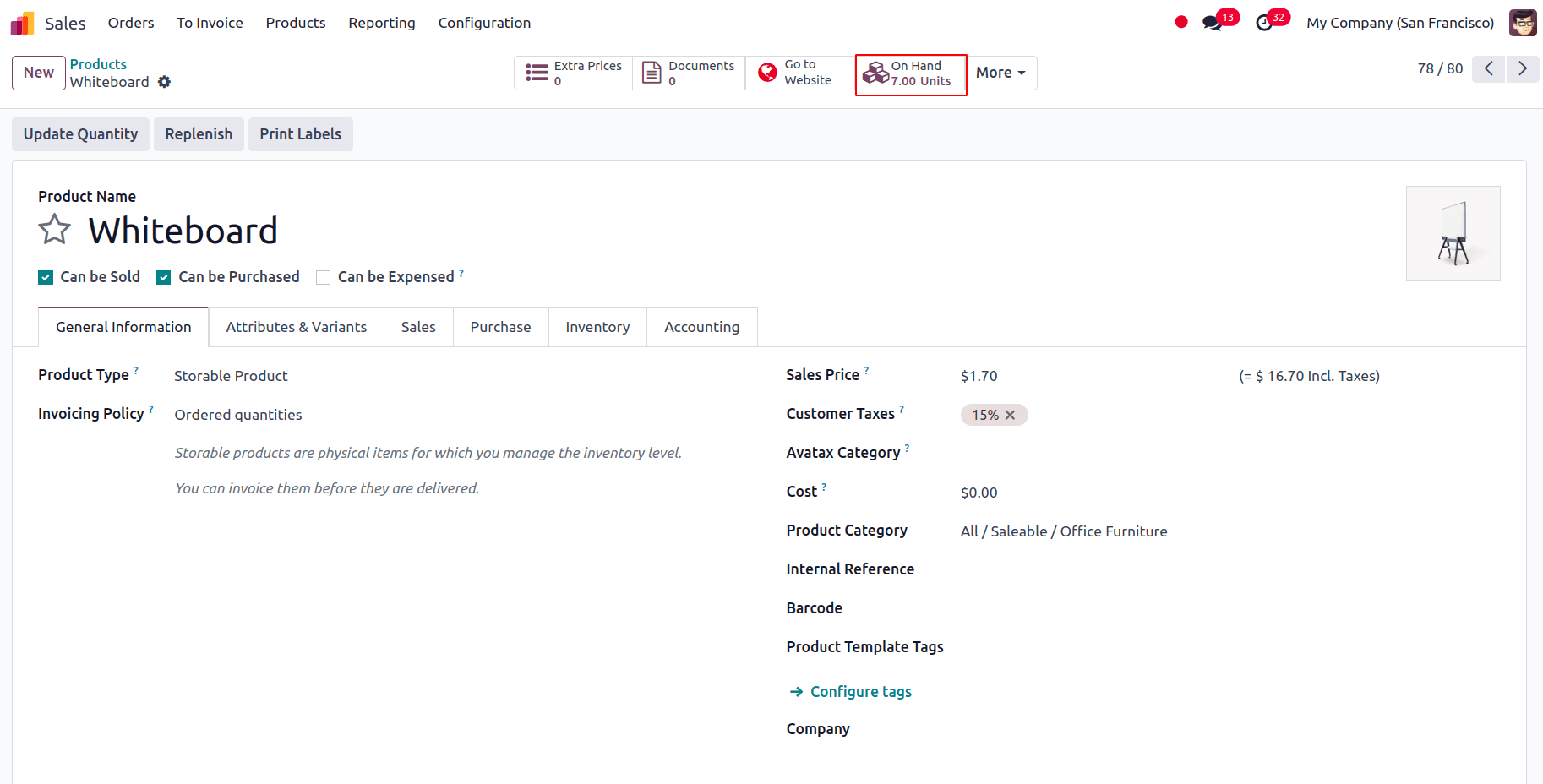
The quantity specified in the sale order is ten pieces. The back order will be generated automatically for the remaining quantity.
Go to the Delivery smart tab, and a new page will appear with the two delivery statuses.
Once the product is in stock, the shipping can be completed.
In the case of Never, no back order is created, and the order for the remaining product quantity is canceled.
Ship all products at once:
In this situation, the products will be dispatched all at once. Consider the following scenario: a product has a stock amount of 10 and we have received an order for 15 of that product.
Then, as per the choosing policy ship all products at once: the order cannot be fulfilled until the stick is replenished and we have the entire amount of the product on hand for which we received the order.
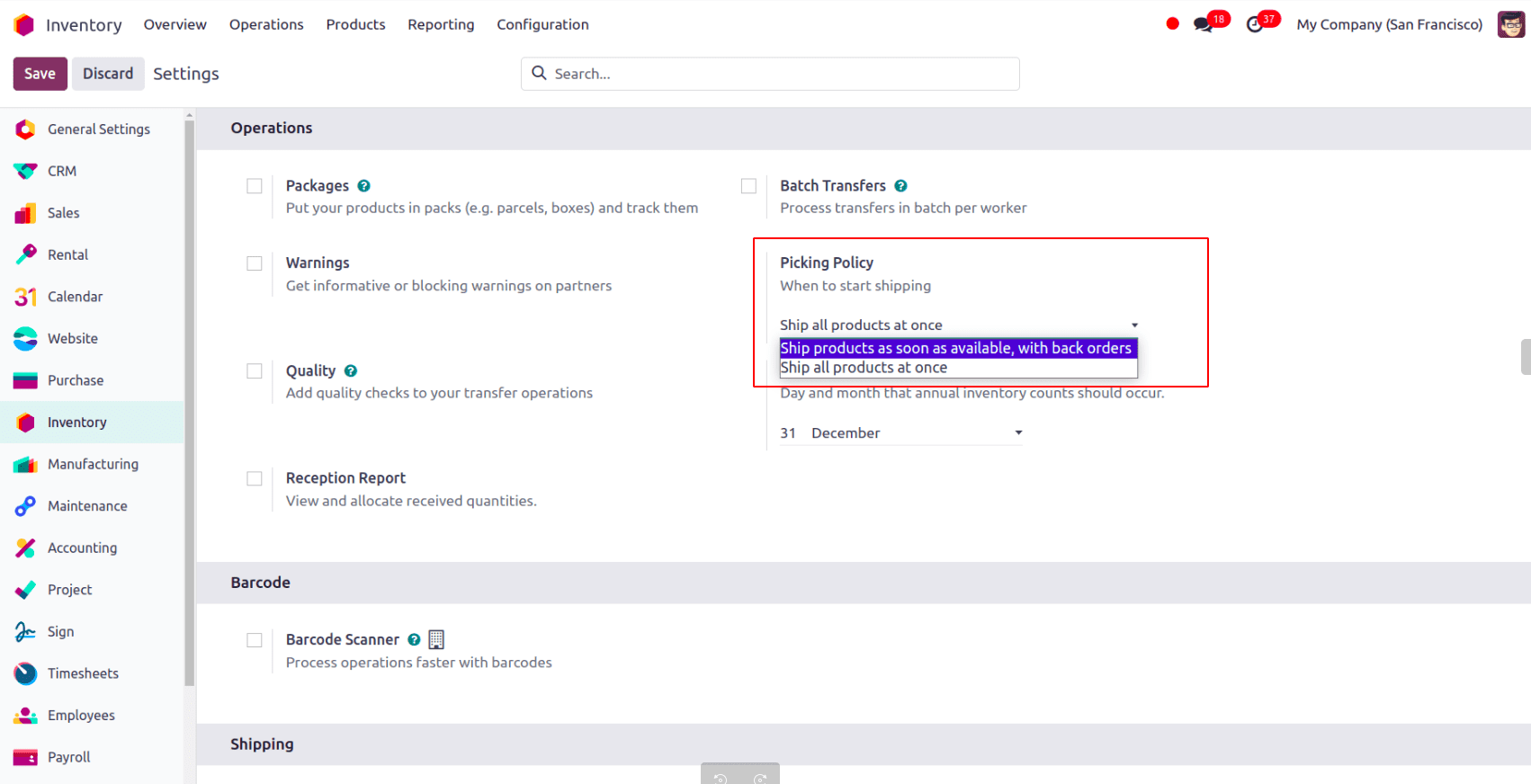
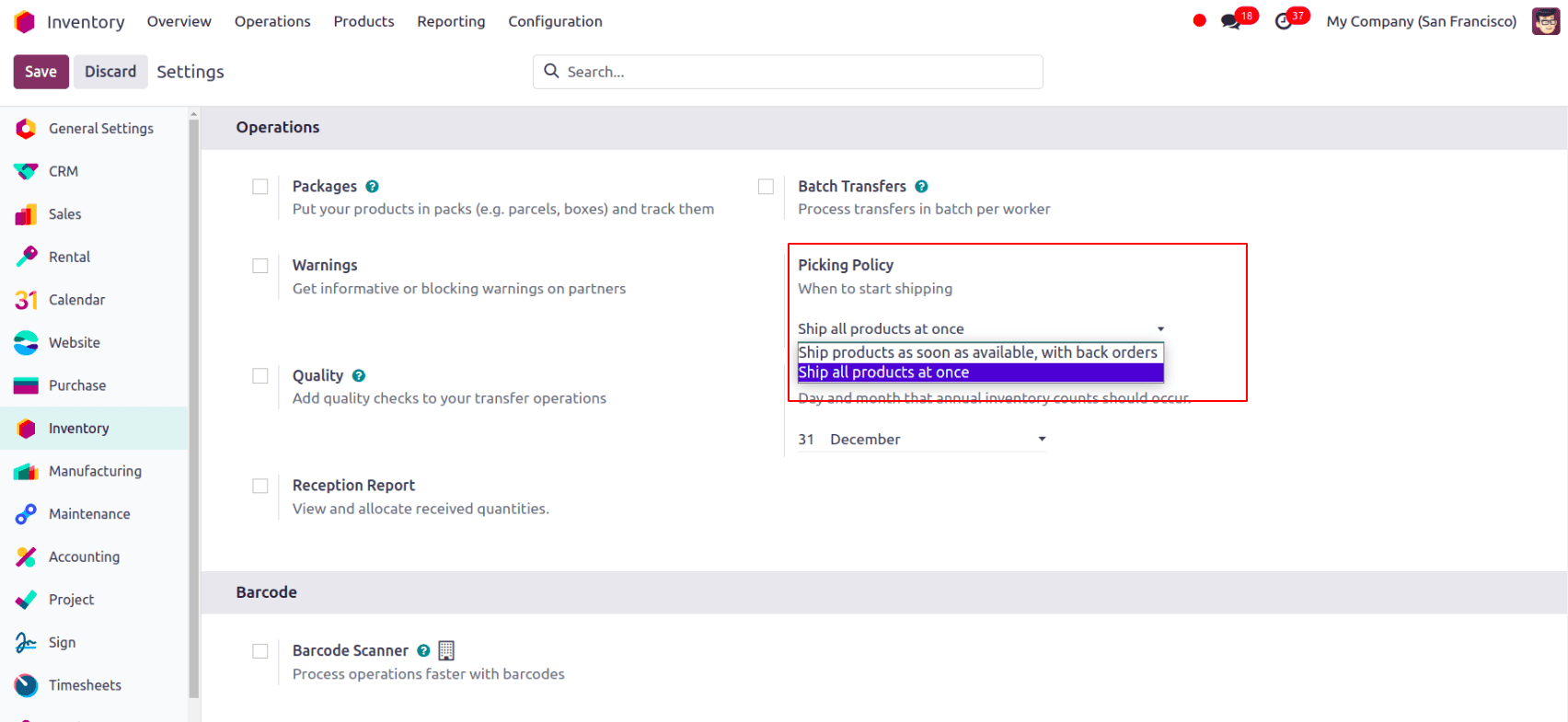
We may configure this in the inventory module by going to Inventory → Configuration → Settings.
There are two picking policy options available: ship products as soon as they become available with back orders or ship all products at once. Select ‘ship all products at once.’
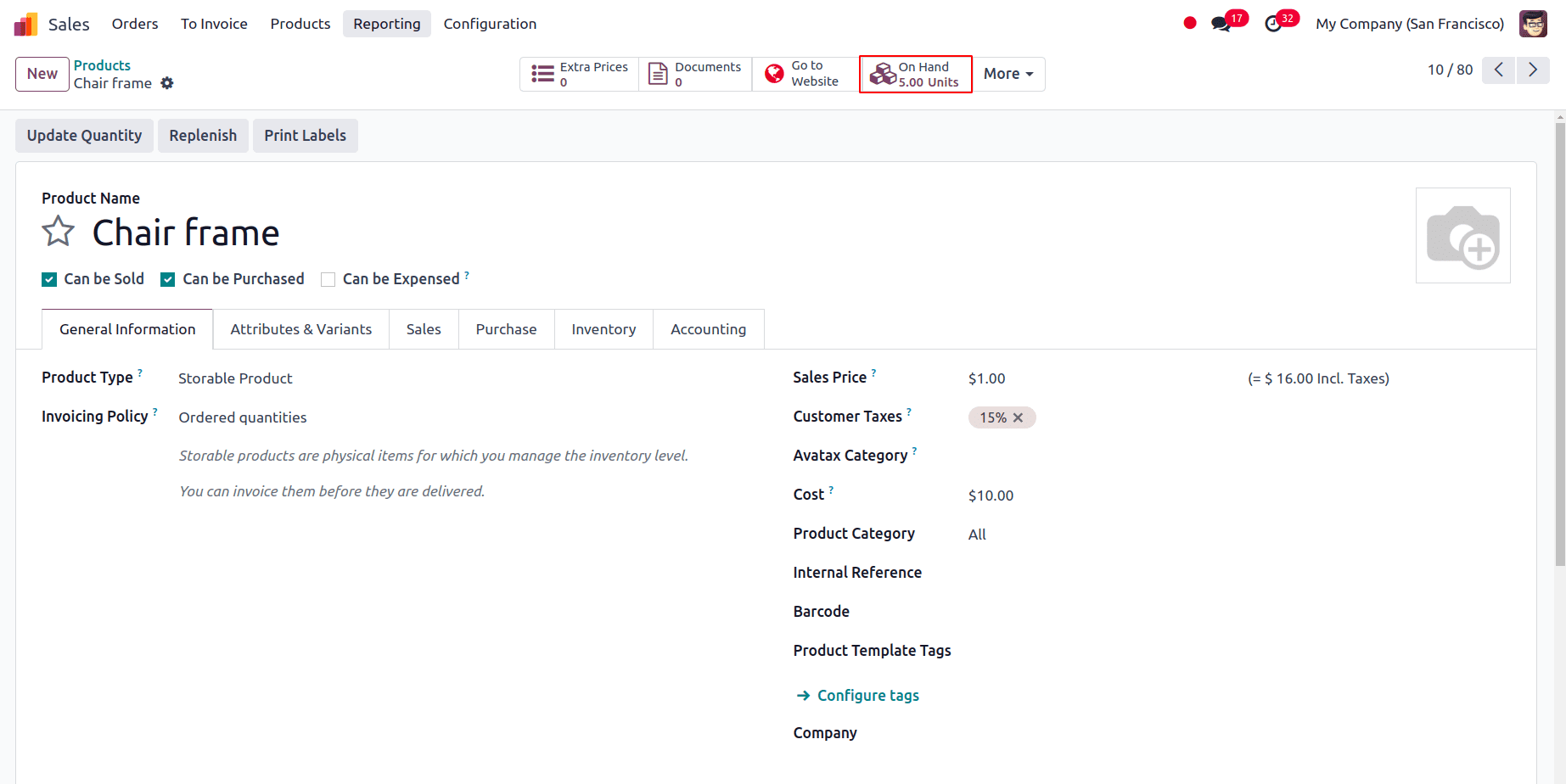
Consider this: We have got an order for the product, chair frame, in ten quantities.
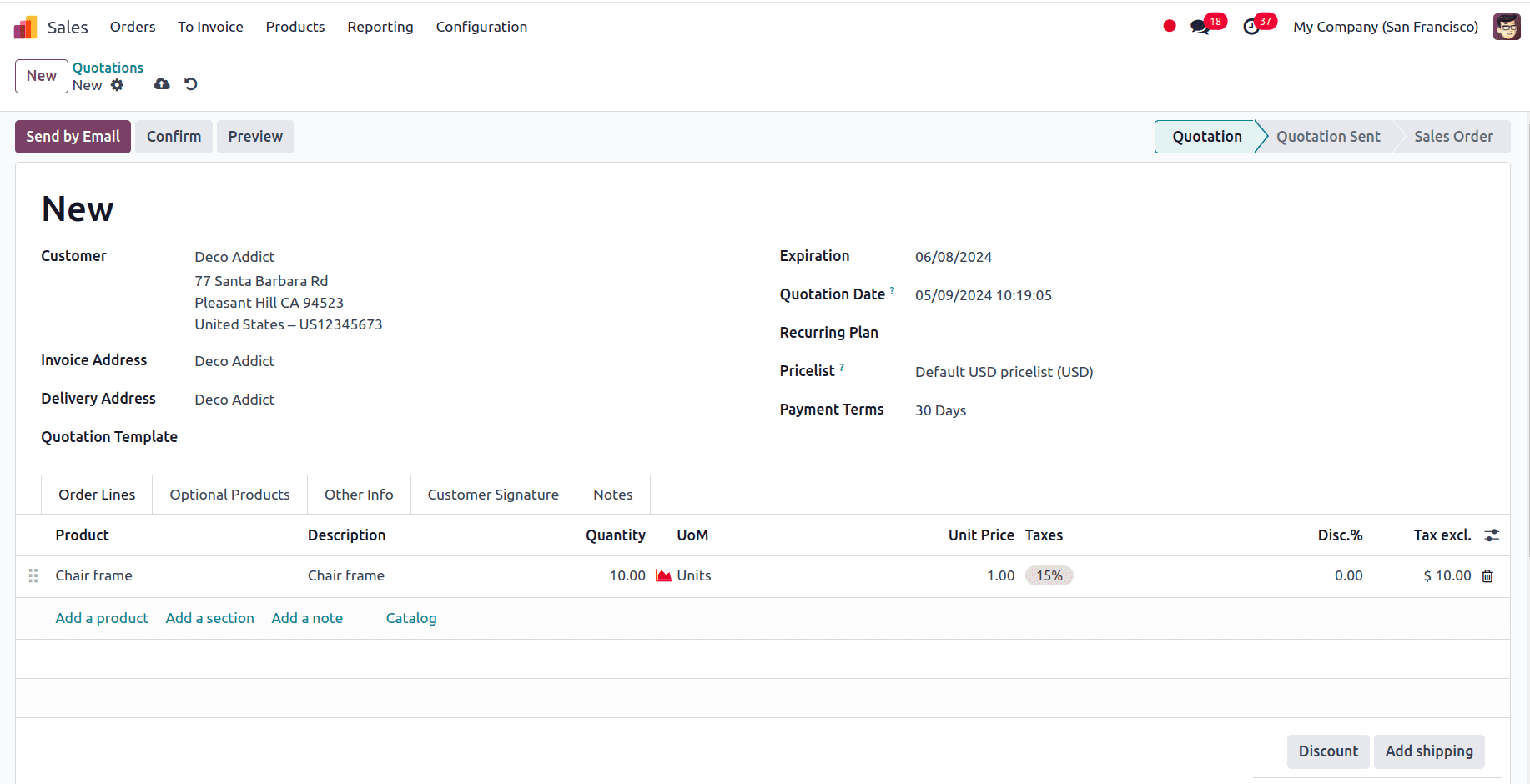
Only 5 units of the product chair frame are currently available in stock.
We can also configure the shipping policy under the sale order’s other information tab.

We can finalize the sales order and proceed to the delivery smart tab.
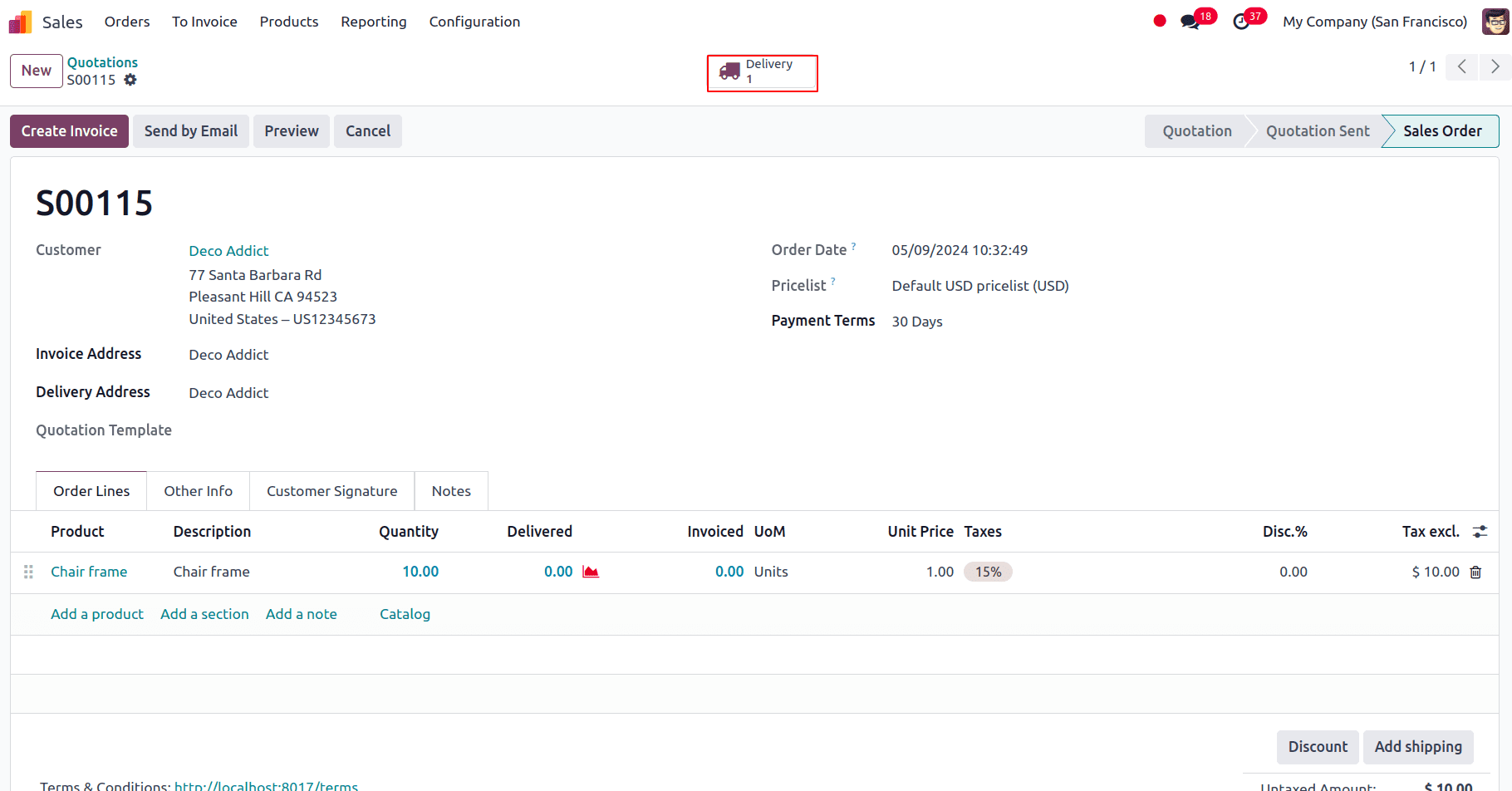
A new page displays, indicating that the delivery status is ‘waiting’ and will only be ready when the products are restocked in stock.
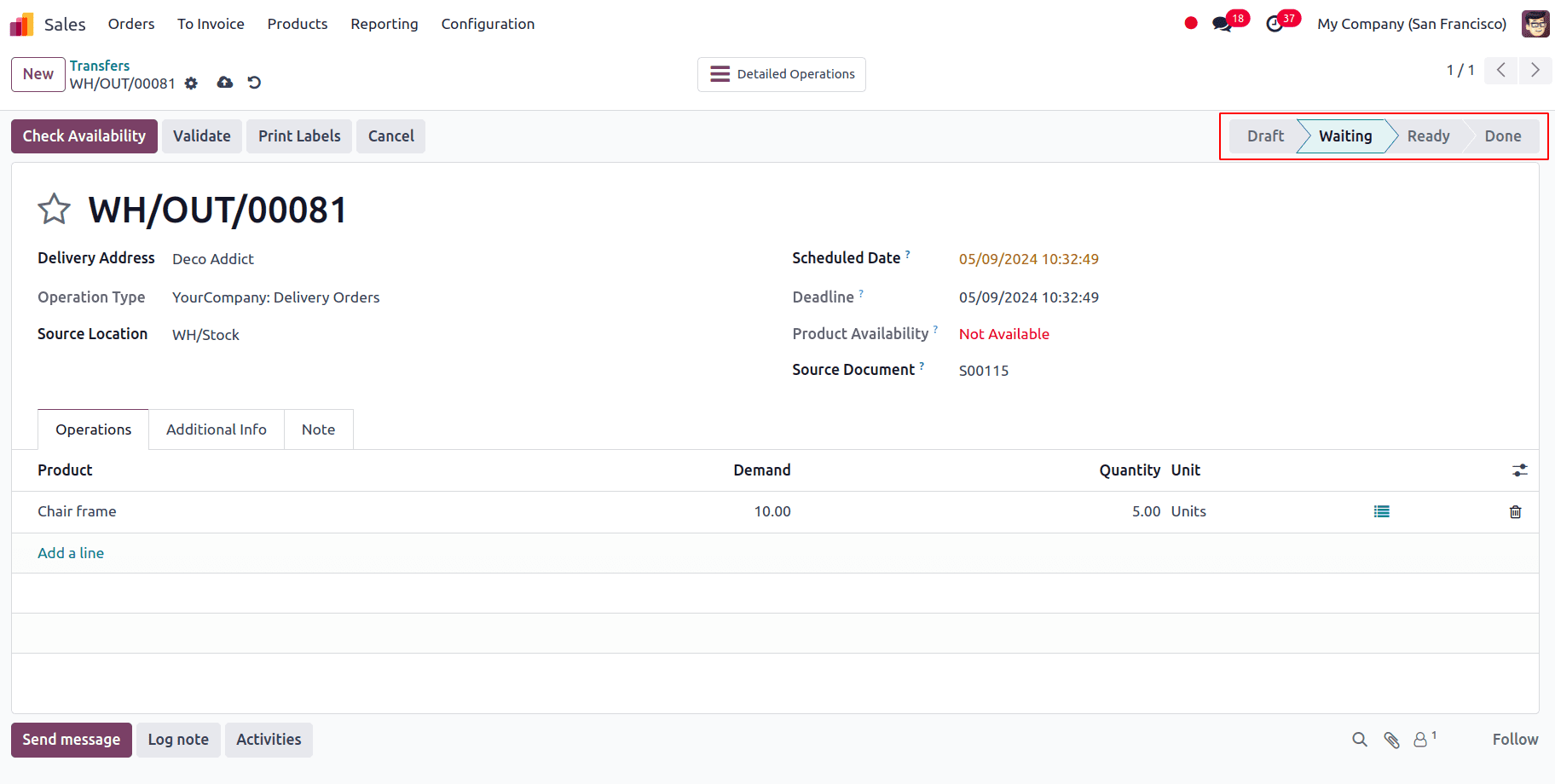
Because we have set the choosing policy to ‘Ship all products at once’, we will be unable to proceed with this sale order until we have the whole quantity required on hand.
In this scenario, the order cannot be executed because the quantity specified in the sales order exceeds the quantity on hand.
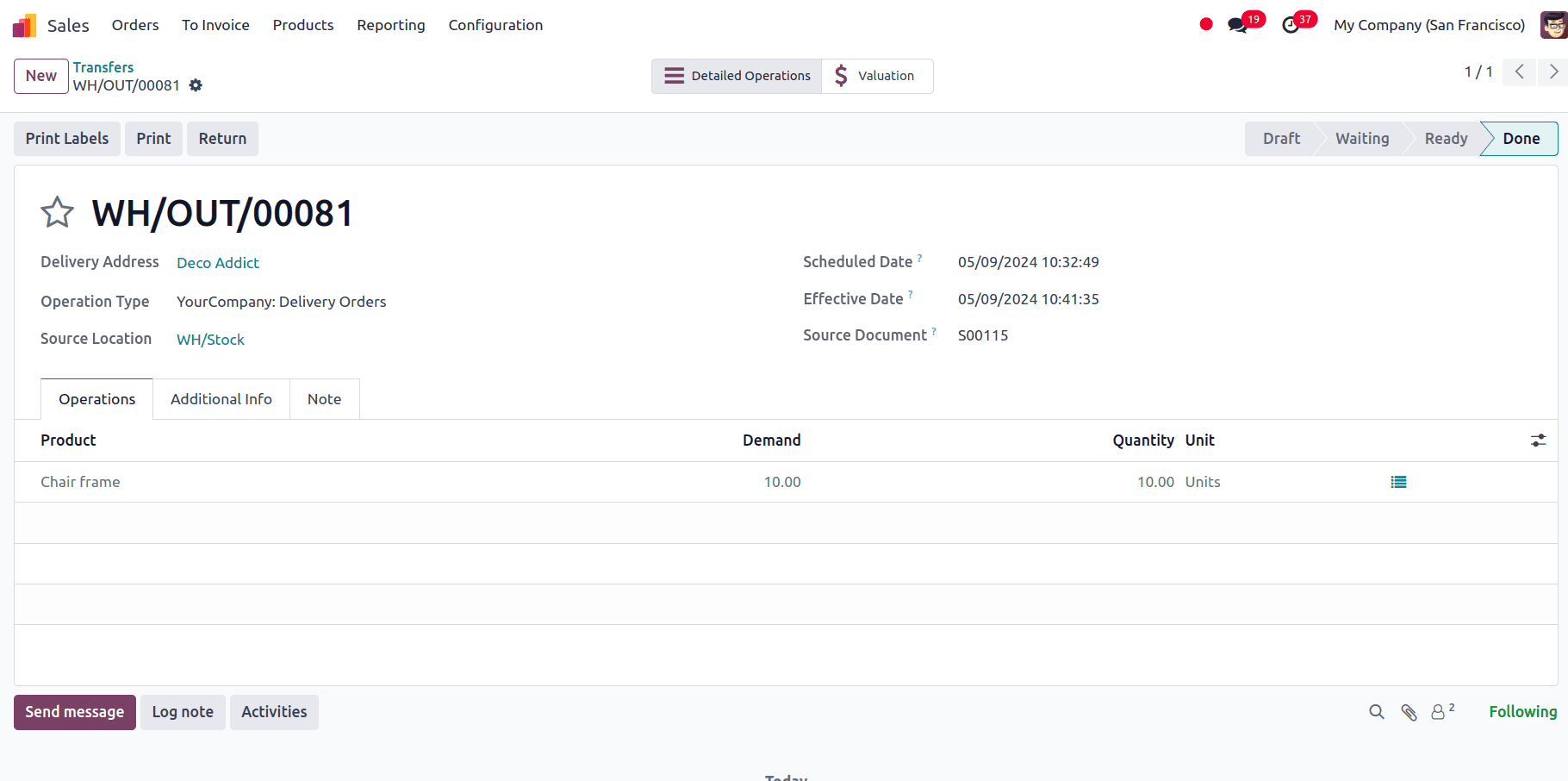
So, after the stock is restocked, the products are shipped all at once in accordance with the picking policy we have set.
So, when the stock is updated, we can see that the delivery is in the ‘Ready’ condition, which allows us to approve the delivery and dispatch the products to clients all at once.
In this blog, we have discussed the two alternatives choosing policies available in Odoo 17 and how they affect the delivery process.
Properly managing Odoo 17 picking process is an important first step toward optimizing shipping processes and improving overall inventory management effectiveness.
Odoo’s broad feature set and customizable choices make it simple to customize your picking process to your specific requirements.
Effective selection criteria are generally applicable to both small startups and large businesses, laying the foundation for success in today’s highly competitive business market.


